目录
- 目录
- RNN
- RNN不能解决长期依赖问题
- LSTM:长短期记忆网络
- LSTM步骤
- LSTM的变种
- pytorch实现单向LSTM
- pytorch实现双向LSTM
- 例子:使用LSTM对语句中的单词进行词性标注
- MNIST数据集上LSTM和CNN的效果对比
- 参考
RNN
- 背景:传统神经网络不具有记忆功能
- 记忆:比如人的思考是基于记忆的知识的
- 方案:RNN
- 将信息持久化
- 可以解决网络的记忆功能
-
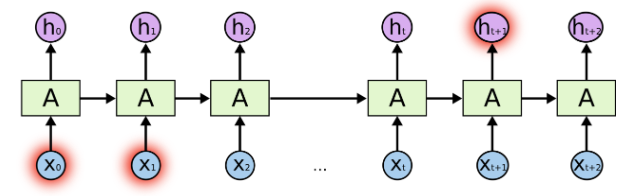
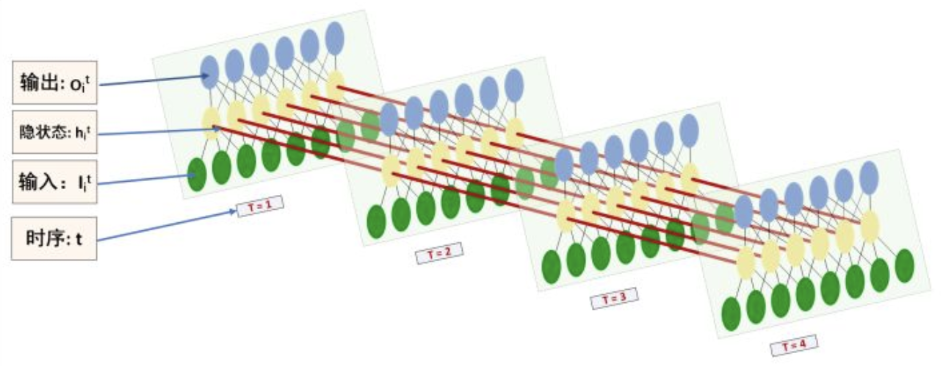
RNN可以看做是同一个网络的多个副本,每一份都将信息传递到下一个副本
- RNN环式结构展开为链式:
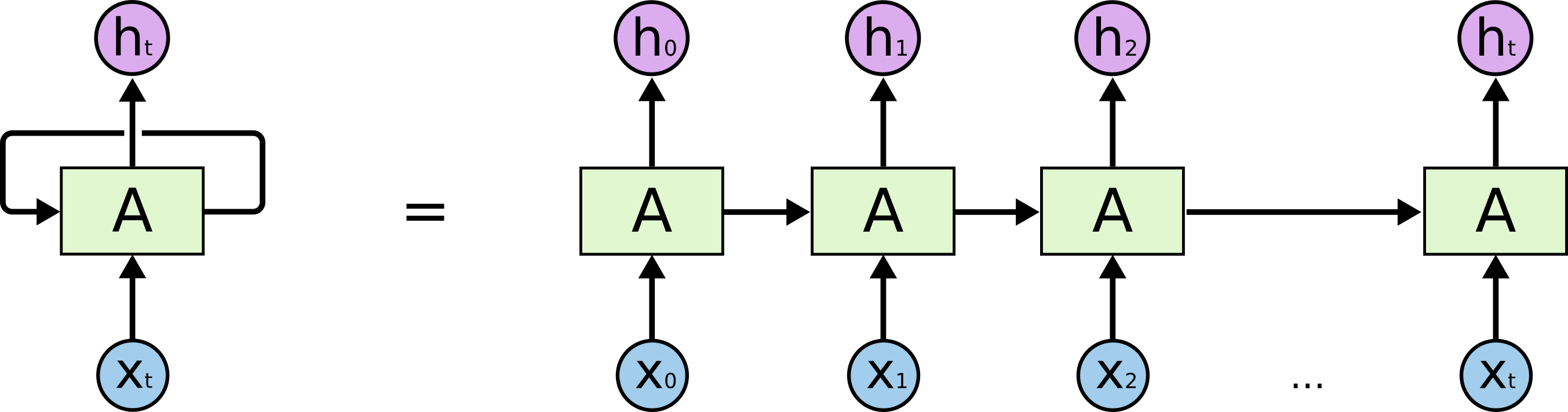
- 链式结构展示了RNN与序列和列表的密切关系
- 语音识别、语言建模、翻译、图片标题取的很好效果
RNN不能解决长期依赖问题
- RNN核心:将以前的信息连接到当前任务中
- 缺点:
- 不能保留更远的上下文信息
- 存在梯度消失和梯度爆炸的问题。当每层的权重W小于1时,误差传到最开始的层,结果接近于0,梯度消失;当每层的权重W大于1时,误差传到最开始的层,结果变得无穷大,梯度爆炸。
- 简单例子:
- 输入:“the clouds are in the xxx”
- 预测:xxx
- RNN:可以训练得很好预测出来,根据上下文,很容易
- 特点:当前位置与相关信息所在位置之间的距离相对较小
- 复杂例子:
- 输入:“I grew up in France… I speak fluent xxx”
- 预测:xxx
- RNN:可以训练得很好预测出来,根据上下文,不能很好的预测出来
- 特点:相关信息和需要该信息的位置之间的距离可能非常的远,此时需要更多的上下文信息才能很好的预测
- 随着距离的增大,RNN对于将这些信息连接起来无能为力
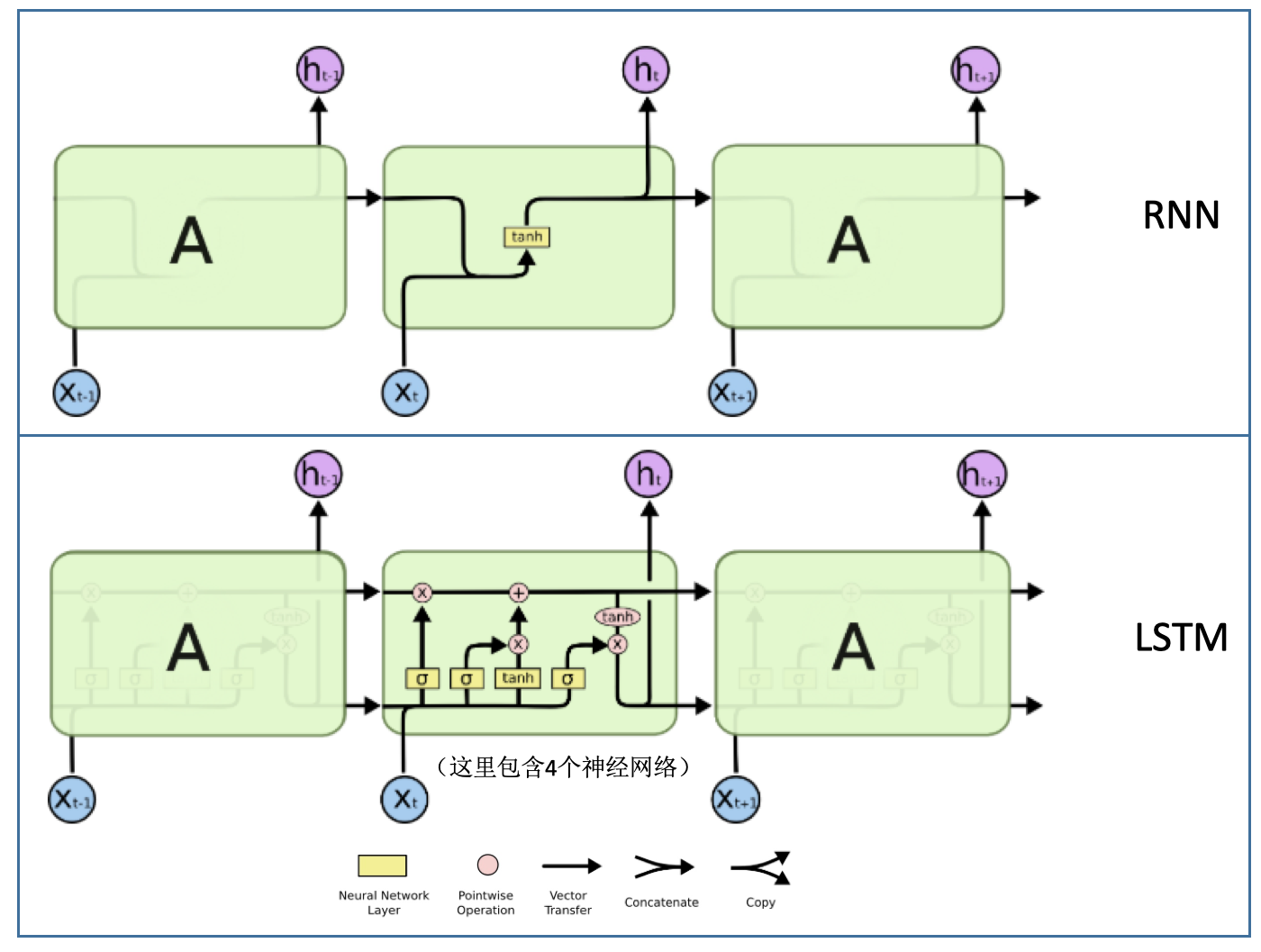
LSTM:长短期记忆网络
- LSTM:long short term memory networks
- 可学习到长期依赖关系
- 目前有很多改进的版本
- 在许多问题上效果很好
- RNN vs LSTM结构:
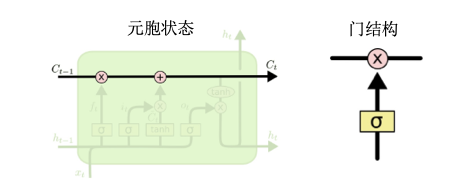
- 核心:元胞状态
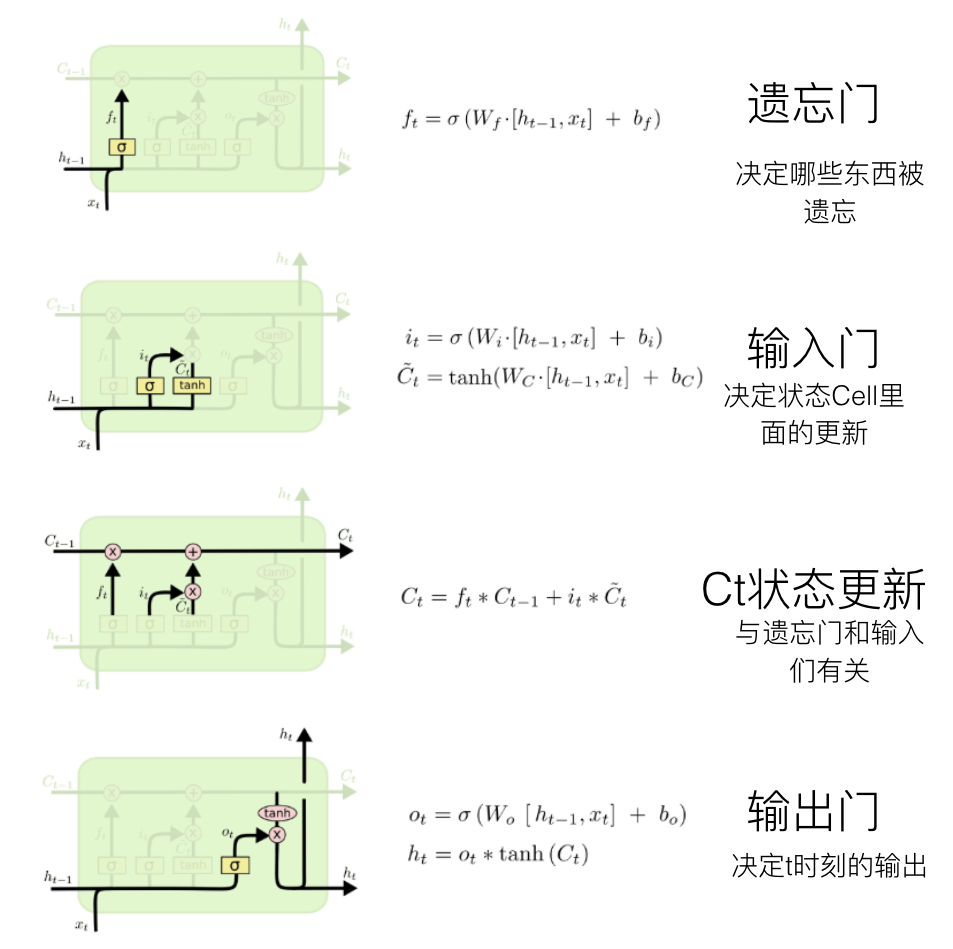
LSTM步骤
LSTM的变种
- GRU模型:Gated Recurrent Unit
- 将遗忘门和输入门合并成为单一的“更新门(Update Gate)”
- 将元胞状态(Cell State)和隐状态(Hidden State)合并
- 比标准的LSTM模型更简化
- 越来越流行

pytorch实现单向LSTM
使用单向LSTM:
nn = nn.LSTM(input_size=10, hidden_size=20, num_layers=2)#(input_size,hidden_size,num_layers)
input = torch.randn(5, 3, 10)#(seq_len, batch, input_size)
h0 = torch.randn(2, 3, 20) #(num_layers,batch,output_size)
c0 = torch.randn(2, 3, 20) #(num_layers,batch,output_size)
output, (hn, cn) = rnn(input, (h0, c0))
output.shape #(seq_len, batch, output_size)
torch.Size([5, 3, 20])
hn.shape #(num_layers, batch, output_size)
torch.Size([2, 3, 20])
cn.shape #(num_layers, batch, output_size)
torch.Size([2, 3, 20])
pytorch实现双向LSTM
rnn = nn.LSTM(input_size=10, hidden_size=20, num_layers=2,bidirectional=True)#(input_size,hidden_size,num_layers)
input = torch.randn(5, 3, 10)#(seq_len, batch, input_size)
h0 = torch.randn(4, 3, 20) #(num_layers,batch,output_size)
c0 = torch.randn(4, 3, 20) #(num_layers,batch,output_size)
output, (hn, cn) = rnn(input, (h0, c0))
output.shape #(seq_len, batch, output_size*2)
torch.Size([5, 3, 40])
hn.shape #(num_layers*2, batch, output_size)
torch.Size([4, 3, 20])
cn.shape #(num_layers*2, batch, output_size)
torch.Size([4, 3, 20])
例子:使用LSTM对语句中的单词进行词性标注
每个单词可以有多个词性,在不同的语境中,其词性是不同的,所以语义分析的一个点就是对任意一句话进行每个单词的词性标注。因为这个是上下文强相关的,所以很适合LSTM模型。
- 输入:一句话,转换后的特征:每个单词在词典中的index值
- 输出:一个矩阵,每个单词所属词性类别的概率,比如一句话总共10个单词,总共有3个词性类别,那么生成的就是一个10x3的矩阵。然后用softmax可以取最大概率值的作为每个词的最后词性标注。
# https://www.pytorchtutorial.com/pytorch-sequence-model-and-lstm-networks/
import torch
import torch.autograd as autograd # torch中自动计算梯度模块
import torch.nn as nn # 神经网络模块
import torch.nn.functional as F # 神经网络模块中的常用功能
import torch.optim as optim # 模型优化器模块
torch.manual_seed(1)
######################
### 定义训练数据
training_data = [
("The dog ate the apple".split(), ["DET", "NN", "V", "DET", "NN"]),
("Everybody read that book".split(), ["NN", "V", "DET", "NN"])
]
######################
### 创建词典:单词词典用于特征生成;词性词典用于label生成
# 创建索引字典(这里是根据训练数据创建的,一般的应该是有一个大而全的词典)
word_to_ix = {} # 单词的索引字典
for sent, tags in training_data:
for word in sent:
if word not in word_to_ix:
word_to_ix[word] = len(word_to_ix)
print(word_to_ix)
# 创建词性的词典
tag_to_ix = {"DET": 0, "NN": 1, "V": 2} # 手工设定词性标签数据字典
# 根据序列和对应的词典,生成对应序列在词典中的index
# sentence+单词词典 =》sentence顺序每个单词的index
# tags+词性词典 =》每个词的词性对应的index
def prepare_sequence(seq, to_ix):
idxs = [to_ix[w] for w in seq]
tensor = torch.LongTensor(idxs)
return autograd.Variable(tensor)
######################
### 定义LSTM网络
class LSTMTagger(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embedding_dim, hidden_dim, vocab_size, tagset_size):
super(LSTMTagger, self).__init__()
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.word_embeddings = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, hidden_dim)
self.hidden2tag = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, tagset_size)
self.hidden = self.init_hidden()
def init_hidden(self):
return (autograd.Variable(torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_dim)),
autograd.Variable(torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_dim)))
def forward(self, sentence):
embeds = self.word_embeddings(sentence)
lstm_out, self.hidden = self.lstm(
embeds.view(len(sentence), 1, -1), self.hidden)
tag_space = self.hidden2tag(lstm_out.view(len(sentence), -1))
tag_scores = F.log_softmax(tag_space)
return tag_scores
######################
### 定义一个具体的LSTM网络:主要是对网络参数进行传值
model = LSTMTagger(2, 3, len(word_to_ix), len(tag_to_ix))
# 定义损失函数
loss_function = nn.NLLLoss()
# 定义优化器
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
######################
### 这里是还没有使用训练数据进行模型训练的结果
# inputs = prepare_sequence(training_data[0][0], word_to_ix)
# tag_scores = model(inputs)
# print(training_data[0][0])
# print(inputs)
# print(tag_scores)
# ['The', 'dog', 'ate', 'the', 'apple']
# tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
# tensor([[-1.6456, -1.0384, -0.7917],
# [-1.6287, -1.1794, -0.7004],
# [-1.6278, -1.2331, -0.6689],
# [-1.6497, -1.1290, -0.7245],
# [-1.6244, -1.2177, -0.6791]], grad_fn=<LogSoftmaxBackward>)
######################
### 使用训练数据进行模型训练
for epoch in range(300): # 我们要训练300次,可以根据任务量的大小酌情修改次数。
print("ecpo:",epoch)
for sentence, tags in training_data:
# 清除网络先前的梯度值,梯度值是Pytorch的变量才有的数据,Pytorch张量没有
model.zero_grad()
# 重新初始化隐藏层数据,避免受之前运行代码的干扰
model.hidden = model.init_hidden()
# 准备网络可以接受的的输入数据和真实标签数据,这是一个监督式学习
# 这里的模型的输入x就是sentence_in,转换后就是句子里每个词在词典里面的index
sentence_in = prepare_sequence(sentence, word_to_ix)
targets = prepare_sequence(tags, tag_to_ix)
# 运行我们的模型,直接将模型名作为方法名看待即可
tag_scores = model(sentence_in)
# 计算损失,反向传递梯度及更新模型参数
loss = loss_function(tag_scores, targets)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
######################
### 检验模型效果:这里用的是训练数据,只为了演示
inputs = prepare_sequence(training_data[0][0], word_to_ix)
tag_scores = model(inputs)
print(tag_scores)
# tensor([[-0.9031, -0.5412, -4.3697],
# [-2.3633, -0.1098, -4.6217],
# [-2.7825, -3.1968, -0.1085],
# [-0.6320, -0.8947, -2.8180],
# [-2.3956, -0.1101, -4.3304]], grad_fn=<LogSoftmaxBackward>)
MNIST数据集上LSTM和CNN的效果对比
使用RNN LSTM也可以对图片进行分类:
- 输入:图片(28x28),转换后的特征,28个连续的序列,每一个是28维的一个向量?
代码:
# CNN:https://github.com/pytorch/examples/blob/master/mnist/main.py
# RNN LSTM:https://github.com/yunjey/pytorch-tutorial/blob/master/tutorials/02-intermediate/recurrent_neural_network/main.py
from __future__ import print_function
import argparse
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 20, 5, 1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(20, 50, 5, 1)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(4*4*50, 500)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(500, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.conv1(x))
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2, 2)
x = F.relu(self.conv2(x))
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2, 2)
x = x.view(-1, 4*4*50)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.fc2(x)
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, num_classes):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, batch_first=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
# Set initial hidden and cell states
h0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_size).to(device)
c0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_size).to(device)
# Forward propagate LSTM
out, _ = self.lstm(x, (h0, c0)) # out: tensor of shape (batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size)
# Decode the hidden state of the last time step
out = self.fc(out[:, -1, :])
return out
# model = RNN(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, num_classes).to(device)
def train(args, model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch):
model.train()
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(data)
loss = F.nll_loss(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch_idx % args.log_interval == 0:
print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, batch_idx * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset),
100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item()))
def train_LSTM(args, model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch, sequence_length, input_size):
model.train()
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
data = data.reshape(-1, sequence_length, input_size).to(device)
target = target.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(data)
# loss = F.nll_loss(output, target) # if use nll_loss for LSTM, will be negative number
loss = criterion(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch_idx % args.log_interval == 0:
print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, batch_idx * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset),
100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item()))
def test(args, model, device, test_loader):
model.eval()
test_loss = 0
correct = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data, target in test_loader:
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
output = model(data)
test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target, reduction='sum').item() # sum up batch loss
pred = output.argmax(dim=1, keepdim=True) # get the index of the max log-probability
correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset)
print('\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\n'.format(
test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset),
100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)))
def test_LSTM(args, model, device, test_loader, sequence_length, input_size):
model.eval()
test_loss = 0
correct = 0
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
with torch.no_grad():
for data, target in test_loader:
data = data.reshape(-1, sequence_length, input_size).to(device)
target = target.to(device)
output = model(data)
# test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target, reduction='sum').item() # sum up batch loss
test_loss += criterion(output, target)
pred = output.argmax(dim=1, keepdim=True) # get the index of the max log-probability
correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset)
print('\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\n'.format(
test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset),
100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)))
def main():
# Training settings
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch MNIST Example')
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=64, metavar='N',
help='input batch size for training (default: 64)')
parser.add_argument('--test-batch-size', type=int, default=1000, metavar='N',
help='input batch size for testing (default: 1000)')
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=10, metavar='N',
help='number of epochs to train (default: 10)')
parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.01, metavar='LR',
help='learning rate (default: 0.01)')
parser.add_argument('--momentum', type=float, default=0.5, metavar='M',
help='SGD momentum (default: 0.5)')
parser.add_argument('--no-cuda', action='store_true', default=False,
help='disables CUDA training')
parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=1, metavar='S',
help='random seed (default: 1)')
parser.add_argument('--log-interval', type=int, default=10, metavar='N',
help='how many batches to wait before logging training status')
parser.add_argument('--save-model', action='store_true', default=False,
help='For Saving the current Model')
args = parser.parse_args()
use_cuda = not args.no_cuda and torch.cuda.is_available()
torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
# device = torch.device("cuda" if use_cuda else "cpu")
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
kwargs = {'num_workers': 1, 'pin_memory': True} if use_cuda else {}
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST('../../data', train=True, download=True,
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])),
batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST('../../data', train=False, transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])),
batch_size=args.test_batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
# CNN
# model = Net().to(device)
# optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=args.lr, momentum=args.momentum)
# for epoch in range(1, args.epochs + 1):
# train(args, model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch)
# test(args, model, device, test_loader)
# RNN LSTM
sequence_length = 28
input_size = 28
hidden_size = 128
num_layers = 2
num_classes = 10
model = RNN(input_size=input_size, hidden_size=hidden_size, num_layers=num_layers, num_classes=num_classes).to(device) # RNN LSTM
# optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=args.lr, momentum=args.momentum)
# SGD works not well for LSTM
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=args.lr)
for epoch in range(1, args.epochs + 1):
train_LSTM(args, model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch, sequence_length, input_size)
test_LSTM(args, model, device, test_loader, sequence_length, input_size)
if (args.save_model):
torch.save(model.state_dict(),"mnist_cnn.pt")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
效果,这里只是测试一下,所以设置了epoch=2,使用更大的值时,效果应该都分别有提升。
# CNN
➜ LSTM git:(master) ✗ CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=3 python mnist.py
Train Epoch: 1 [0/60000 (0%)] Loss: 2.300039
Train Epoch: 1 [640/60000 (1%)] Loss: 2.213470
Train Epoch: 1 [1280/60000 (2%)] Loss: 2.170460
Train Epoch: 1 [1920/60000 (3%)] Loss: 2.076699
...
Train Epoch: 1 [57600/60000 (96%)] Loss: 0.117136
Train Epoch: 1 [58240/60000 (97%)] Loss: 0.191664
Train Epoch: 1 [58880/60000 (98%)] Loss: 0.204842
Train Epoch: 1 [59520/60000 (99%)] Loss: 0.064107
Test set: Average loss: 0.1015, Accuracy: 9661/10000 (97%)
Train Epoch: 2 [0/60000 (0%)] Loss: 0.145626
Train Epoch: 2 [640/60000 (1%)] Loss: 0.119849
Train Epoch: 2 [1280/60000 (2%)] Loss: 0.101394
Train Epoch: 2 [1920/60000 (3%)] Loss: 0.068628
...
Train Epoch: 2 [57600/60000 (96%)] Loss: 0.037703
Train Epoch: 2 [58240/60000 (97%)] Loss: 0.166170
Train Epoch: 2 [58880/60000 (98%)] Loss: 0.035417
Train Epoch: 2 [59520/60000 (99%)] Loss: 0.069601
Test set: Average loss: 0.0610, Accuracy: 9829/10000 (98%)
# RNN LSTM
➜ LSTM git:(master) ✗ CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2 python mnist.py
Train Epoch: 1 [0/60000 (0%)] Loss: -0.016249
Train Epoch: 1 [640/60000 (1%)] Loss: -0.056388
Train Epoch: 1 [1280/60000 (2%)] Loss: -0.091170
Train Epoch: 1 [1920/60000 (3%)] Loss: -0.088119
...
Train Epoch: 1 [57600/60000 (96%)] Loss: -161.295212
Train Epoch: 1 [58240/60000 (97%)] Loss: -165.509781
Train Epoch: 1 [58880/60000 (98%)] Loss: -168.507706
Train Epoch: 1 [59520/60000 (99%)] Loss: -168.760498
Test set: Average loss: -171.4964, Accuracy: 1135/10000 (11%)
Train Epoch: 2 [0/60000 (0%)] Loss: -172.674515
Train Epoch: 2 [640/60000 (1%)] Loss: -172.516800
Train Epoch: 2 [1280/60000 (2%)] Loss: -179.091690
Train Epoch: 2 [1920/60000 (3%)] Loss: -181.107941
...
Train Epoch: 2 [57600/60000 (96%)] Loss: -406.059845
Train Epoch: 2 [58240/60000 (97%)] Loss: -407.615234
Train Epoch: 2 [58880/60000 (98%)] Loss: -407.243866
Train Epoch: 2 [59520/60000 (99%)] Loss: -412.519165
Test set: Average loss: -414.2386, Accuracy: 1135/10000 (11%)
可以看到,上面的loss为负值,说明程序出现了问题,原因是使用的优化器不够好,我们可以选用Adam优化器,而不是SGD。
➜ LSTM git:(master) ✗ CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2 python mnist.py --batch-size 100 --test-batch-size 100 --lr 0.01 --epochs 2
Train Epoch: 1 [0/60000 (0%)] Loss: 2.306968
Train Epoch: 1 [1000/60000 (2%)] Loss: 2.027250
Train Epoch: 1 [2000/60000 (3%)] Loss: 1.387051
Train Epoch: 1 [3000/60000 (5%)] Loss: 1.275983
Train Epoch: 1 [4000/60000 (7%)] Loss: 1.040894
...
Train Epoch: 1 [56000/60000 (93%)] Loss: 0.130190
Train Epoch: 1 [57000/60000 (95%)] Loss: 0.231418
Train Epoch: 1 [58000/60000 (97%)] Loss: 0.111383
Train Epoch: 1 [59000/60000 (98%)] Loss: 0.119482
Test set: Average loss: 0.0011, Accuracy: 9673/10000 (97%)
Train Epoch: 2 [0/60000 (0%)] Loss: 0.136026
Train Epoch: 2 [1000/60000 (2%)] Loss: 0.137714
Train Epoch: 2 [2000/60000 (3%)] Loss: 0.075271
Train Epoch: 2 [3000/60000 (5%)] Loss: 0.187317
Train Epoch: 2 [4000/60000 (7%)] Loss: 0.048653
...
Train Epoch: 2 [56000/60000 (93%)] Loss: 0.072240
Train Epoch: 2 [57000/60000 (95%)] Loss: 0.142520
Train Epoch: 2 [58000/60000 (97%)] Loss: 0.048884
Train Epoch: 2 [59000/60000 (98%)] Loss: 0.139993
Test set: Average loss: 0.0009, Accuracy: 9732/10000 (97%)
直接执行参考脚本效果如下:
# RNN LSTM:https://github.com/yunjey/pytorch-tutorial/blob/master/tutorials/02-intermediate/recurrent_neural_network/main.py
➜ LSTM git:(master) ✗ CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2 python main.py
Epoch [1/2], Step [100/600], Loss: 0.5705
Epoch [1/2], Step [200/600], Loss: 0.3457
Epoch [1/2], Step [300/600], Loss: 0.1618
Epoch [1/2], Step [400/600], Loss: 0.1454
Epoch [1/2], Step [500/600], Loss: 0.1483
Epoch [1/2], Step [600/600], Loss: 0.1474
Epoch [2/2], Step [100/600], Loss: 0.0638
Epoch [2/2], Step [200/600], Loss: 0.0776
Epoch [2/2], Step [300/600], Loss: 0.0269
Epoch [2/2], Step [400/600], Loss: 0.0607
Epoch [2/2], Step [500/600], Loss: 0.0225
Epoch [2/2], Step [600/600], Loss: 0.1379
Test Accuracy of the model on the 10000 test images: 97.1 %
参考
If you link this blog, please refer to this page, thanks!
Post link:https://tsinghua-gongjing.github.io/posts/LSTM.html
Previous:
Run jobs on GPU server
Latest articles
Links
- ZhangLab , RISE database , THU life , THU info
- Data analysis: pandas , numpy , scipy
- ML/DL: sklearn , sklearn(中文) , pytorch
- Visualization: seaborn , matplotlib , gallery
- Github: me