目录
- 目录
- 1. 管道pipeline
- 2. 管道用法:构造
- 3. 管道用法:访问
- 4. 管道用法:访问和设置评估器的参数
- 5. 缓存转换器
- 6. 目标转换:对预测值y进行转换
- 7. 特征联合
- 8. 异构数据的列转换器
- 参考
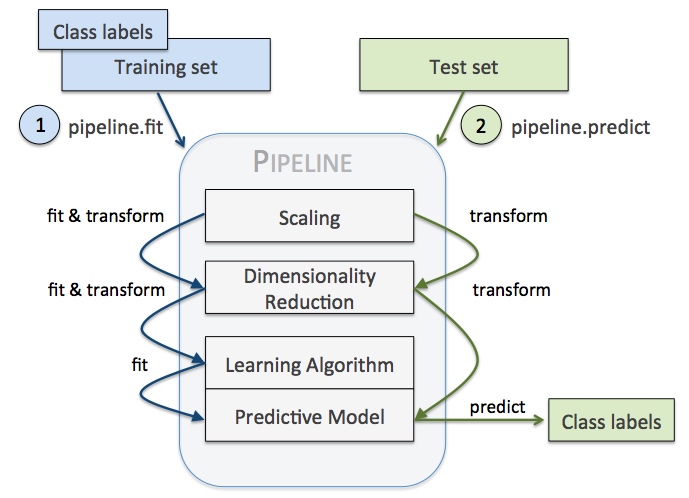
1. 管道pipeline
用途:把多个评估器链接成一个
目的:
- 便捷和封装:只需对数据调用
fit和predict一次,完成所有评估器的适配 - 联合的参数选择:在
grid search时可以一次评估管道中所有评估器的参数 - 安全性:转换与预测都是相同样本,防止测试数据泄露到验证数据中
# 不使用管道
vect = CountVectorizer()
tfidf = TfidfTransformer()
clf = SGDClassifier()
vX = vect.fit_transform(Xtrain)
tfidfX = tfidf.fit_transform(vX)
predicted = clf.fit_predict(tfidfX)
# Now evaluate all steps on test set
vX = vect.fit_transform(Xtest)
tfidfX = tfidf.fit_transform(vX)
predicted = clf.fit_predict(tfidfX)
# 使用管道
pipeline = Pipeline([
('vect', CountVectorizer()),
('tfidf', TfidfTransformer()),
('clf', SGDClassifier()),
])
predicted = pipeline.fit(Xtrain).predict(Xtrain)
# Now evaluate all steps on test set
predicted = pipeline.predict(Xtest)
2. 管道用法:构造
两种构造管道的方式:
- 通过键值对直接构造,把不同的评估器放在列表中
- 通过功能函数
make_pipeline构造
>>> from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
>>> from sklearn.svm import SVC
>>> from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
# 键值对直接构造
>>> estimators = [('reduce_dim', PCA()), ('clf', SVC())]
>>> pipe = Pipeline(estimators)
# 功能函数`make_pipeline`构造
>>> make_pipeline(PCA(), SVC())
>>> pipe
Pipeline(memory=None,
steps=[('reduce_dim', PCA(copy=True,...)),
('clf', SVC(C=1.0,...))], verbose=False)
3. 管道用法:访问
不同的访问构建的评估器的方法(比如查看不同评估器的先后顺序,某个评估器的具体参数值等):
- 构造的各个评估器作为列表保存在属性
steps中,可索引或名称访问 - 直接对管道进行索引或切片访问
# steps属性索引
>>> pipe.steps[0]
('reduce_dim', PCA(copy=True, iterated_power='auto', n_components=None,
random_state=None, svd_solver='auto', tol=0.0,
whiten=False))
# 管道直接索引
>>> pipe[0]
PCA(copy=True, iterated_power='auto', n_components=None, random_state=None,
svd_solver='auto', tol=0.0, whiten=False)
# 管道名称索引
>>> pipe['reduce_dim']
PCA(copy=True, ...)
# 管道切片索引,类似于列表
>>> pipe[:1]
Pipeline(memory=None, steps=[('reduce_dim', PCA(copy=True, ...))],...)
>>> pipe[-1:]
Pipeline(memory=None, steps=[('clf', SVC(C=1.0, ...))],...)
4. 管道用法:访问和设置评估器的参数
参数访问:评估器+两个下划线+参数名称 <estimater>__<parameter>
# 设置评估器clf的参数C
>>> pipe.set_params(clf__C=10)
Pipeline(memory=None,
steps=[('reduce_dim', PCA(copy=True, iterated_power='auto',...)),
('clf', SVC(C=10, cache_size=200, class_weight=None,...))],
verbose=False)
# 网格搜索时同时指定不同评估器的参数
>>> from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
>>> param_grid = dict(reduce_dim__n_components=[2, 5, 10],
... clf__C=[0.1, 10, 100])
>>> grid_search = GridSearchCV(pipe, param_grid=param_grid)
5. 缓存转换器
指定memory参数,可以在fit后缓存每个转换器,如果后面参数和数据相同,可以从缓存调用:
>>> from tempfile import mkdtemp
>>> from shutil import rmtree
>>> from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
>>> from sklearn.svm import SVC
>>> from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
>>> estimators = [('reduce_dim', PCA()), ('clf', SVC())]
>>> cachedir = mkdtemp()
# 指定缓存目录
>>> pipe = Pipeline(estimators, memory=cachedir)
>>> pipe
Pipeline(...,
steps=[('reduce_dim', PCA(copy=True,...)),
('clf', SVC(C=1.0,...))], verbose=False)
>>> # Clear the cache directory when you don't need it anymore
>>> rmtree(cachedir)
6. 目标转换:对预测值y进行转换
TransformedTargetRegressor:在拟合回归模型之前对目标y进行转换
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
>>> from sklearn.compose import TransformedTargetRegressor
>>> from sklearn.preprocessing import QuantileTransformer
>>> from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
>>> from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
>>> boston = load_boston()
>>> X = boston.data
>>> y = boston.target
>>> transformer = QuantileTransformer(output_distribution='normal')
>>> regressor = LinearRegression()
>>> regr = TransformedTargetRegressor(regressor=regressor,
... transformer=transformer)
>>> X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
# 对目标y进行对数转换作为预测值
>>> regr.fit(X_train, y_train)
TransformedTargetRegressor(...)
>>> print('R2 score: {0:.2f}'.format(regr.score(X_test, y_test)))
R2 score: 0.67
# 直接原始的预测值
>>> raw_target_regr = LinearRegression().fit(X_train, y_train)
>>> print('R2 score: {0:.2f}'.format(raw_target_regr.score(X_test, y_test)))
R2 score: 0.64
7. 特征联合
用途:合并多个转换器形成一个新的转换器
>>> from sklearn.pipeline import FeatureUnion
>>> from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
>>> from sklearn.decomposition import KernelPCA
>>> estimators = [('linear_pca', PCA()), ('kernel_pca', KernelPCA())]
>>> combined = FeatureUnion(estimators)
>>> combined
FeatureUnion(n_jobs=None,
transformer_list=[('linear_pca', PCA(copy=True,...)),
('kernel_pca', KernelPCA(alpha=1.0,...))],
transformer_weights=None, verbose=False)
8. 异构数据的列转换器
用途:
- 对数据不同的特征(列)进行不同的变换
- 不存在数据泄露
- 参数化评估
下面的例子是将数据X的
city列进行类别编码title列进行单词向量化
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> X = pd.DataFrame(
... {'city': ['London', 'London', 'Paris', 'Sallisaw'],
... 'title': ["His Last Bow", "How Watson Learned the Trick",
... "A Moveable Feast", "The Grapes of Wrath"],
... 'expert_rating': [5, 3, 4, 5],
... 'user_rating': [4, 5, 4, 3]})
>>> from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer
>>> from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
>>> column_trans = ColumnTransformer(
... [('city_category', CountVectorizer(analyzer=lambda x: [x]), 'city'),
... ('title_bow', CountVectorizer(), 'title')],
... remainder='drop')
# 这里使用的remainder='drop'
# 那么其他的特征列是不输出的
# 通常情况并不想这样的
>>> column_trans.fit(X)
ColumnTransformer(n_jobs=None, remainder='drop', sparse_threshold=0.3,
transformer_weights=None,
transformers=...)
>>> column_trans.get_feature_names()
...
['city_category__London', 'city_category__Paris', 'city_category__Sallisaw',
'title_bow__bow', 'title_bow__feast', 'title_bow__grapes', 'title_bow__his',
'title_bow__how', 'title_bow__last', 'title_bow__learned', 'title_bow__moveable',
'title_bow__of', 'title_bow__the', 'title_bow__trick', 'title_bow__watson',
'title_bow__wrath']
>>> column_trans.transform(X).toarray()
...
array([[1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1]]...)
将ColumnTransformer的remainder=’passthrough’,可以在对某些列特征进行变换的同时,保留其他的特征列的数据(非原位的,其他的列加在转换的末尾),这通常是我们想要的:
>>> column_trans = ColumnTransformer(
... [('city_category', OneHotEncoder(dtype='int'),['city']),
... ('title_bow', CountVectorizer(), 'title')],
... remainder='passthrough')
>>> column_trans.fit_transform(X)
...
array([[1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 5, 4],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 3, 5],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4, 4],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 5, 3]]...)
也可以将某个变换应用于所有非指定的列,比如下面对其他的列都进行MinMaxScaler变换:
>>> from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
>>> column_trans = ColumnTransformer(
... [('city_category', OneHotEncoder(), ['city']),
... ('title_bow', CountVectorizer(), 'title')],
... remainder=MinMaxScaler())
>>> column_trans.fit_transform(X)[:, -2:]
...
array([[1. , 0.5],
[0. , 1. ],
[0.5, 0.5],
[1. , 0. ]])
函数make_column_transformer也可以用于构造列转换:
>>> from sklearn.compose import make_column_transformer
>>> column_trans = make_column_transformer(
... (OneHotEncoder(), ['city']),
... (CountVectorizer(), 'title'),
... remainder=MinMaxScaler())
>>> column_trans
ColumnTransformer(n_jobs=None, remainder=MinMaxScaler(copy=True, ...),
sparse_threshold=0.3,
transformer_weights=None,
transformers=[('onehotencoder', ...)
参考
If you link this blog, please refer to this page, thanks!
Post link:https://tsinghua-gongjing.github.io/posts/sklearn_pipeline.html
Previous:
SQL常见问题
Next:
[CS229] resource
Latest articles
Links
- ZhangLab , RISE database , THU life , THU info
- Data analysis: pandas , numpy , scipy
- ML/DL: sklearn , sklearn(中文) , pytorch
- Visualization: seaborn , matplotlib , gallery
- Github: me