狄克斯特拉算法
- vs 广度优先搜索:
- BFS:寻找最短的段数的路径
- Dijkstra:带权重的图,找到加权最小的路径
- 步骤:
- 1)找出“最便宜”的节点,即可在最短时间到达的
- 2)更新该节点的邻居的开销。即如果有经过当前最便宜节点到达邻居节点的更小值,则更新邻居节点的开销。
- 3)重复上述过程,直到对图中的每个节点都这样做了
- 4)计算最终路径
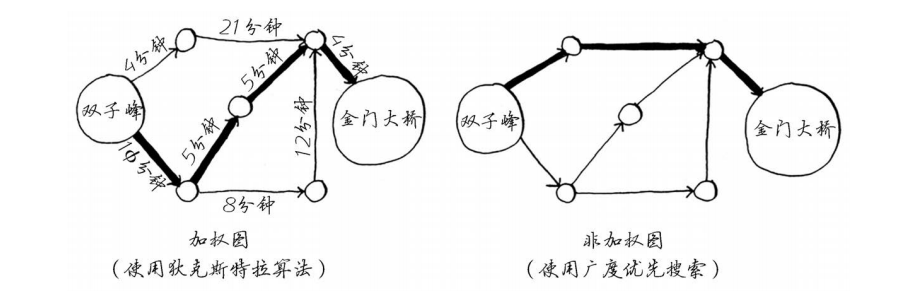
- 例子:
- 下面是前三步确定到每个节点的最小距离

- 狄克斯特拉:总权重最小
- 广度优先搜索:段数最少
术语
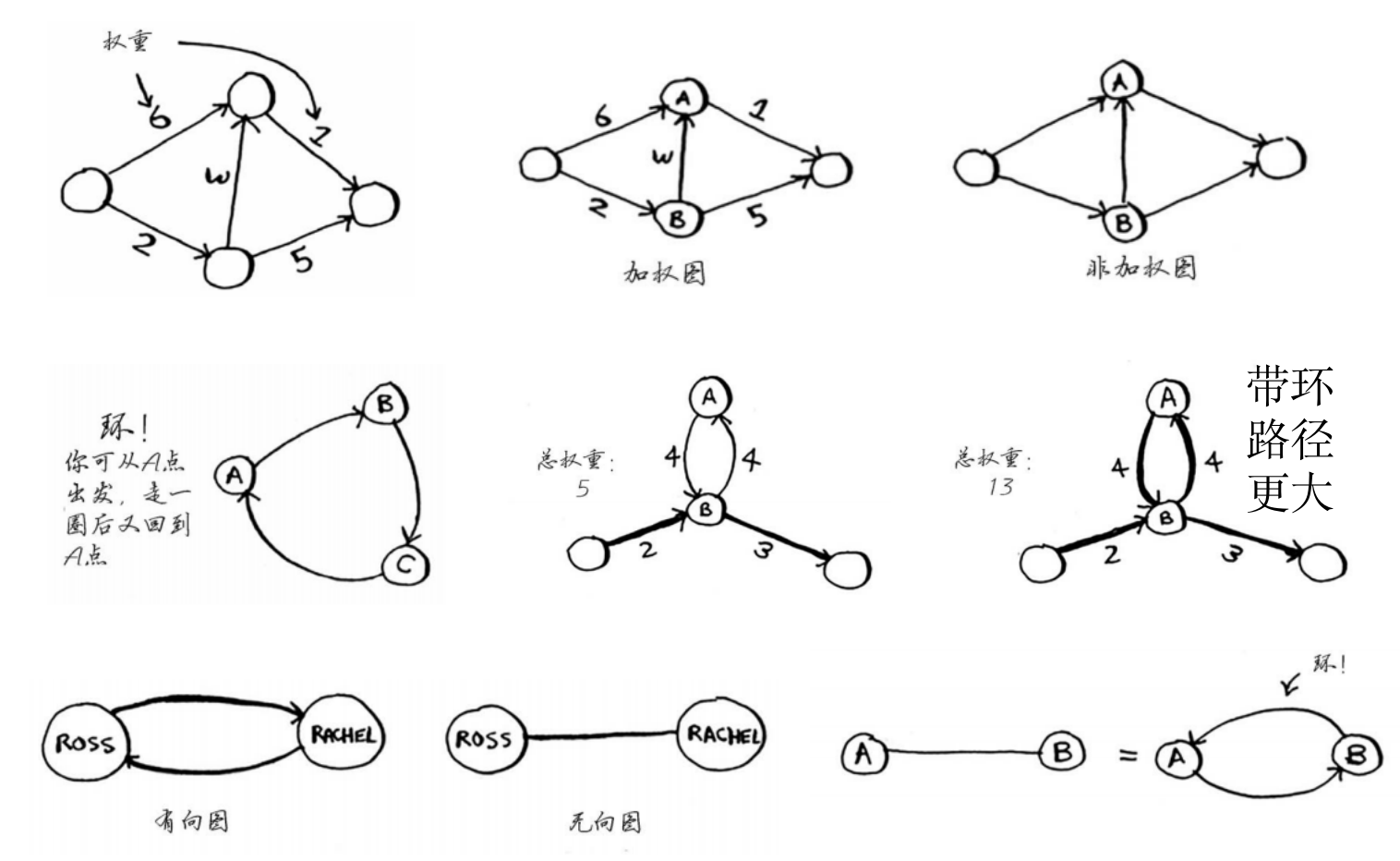
- 权重:图中每条边有关的数字
- 加权图:weighted graph,带权重的图
- 最短路径:使用狄克斯特拉算法
- 非加权图:unweighted graph,不带权重的图
- 最短路径:使用广度优先搜索
- 环:从某一点出发,又可以回到该点
- 绕环的路径增加了权重
- 不可能是最短的路径
- 无向:两个节点彼此指向对方,其实就是环
- 无向图:每条边其实就是一个环。
- 有向无环图:directed acyclic graph,DAG,狄克斯特拉算法仅适用于此
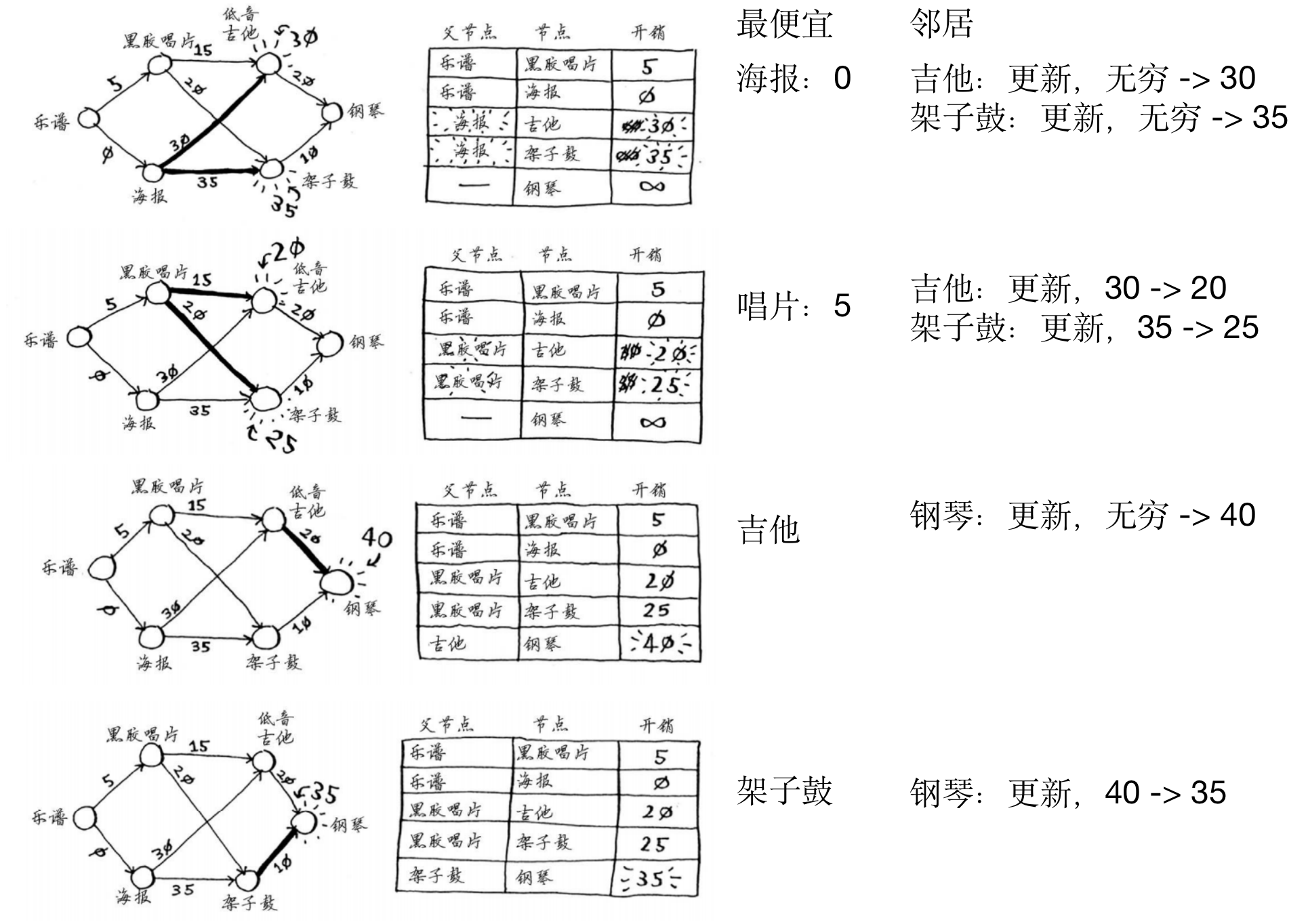
应用:换钢琴
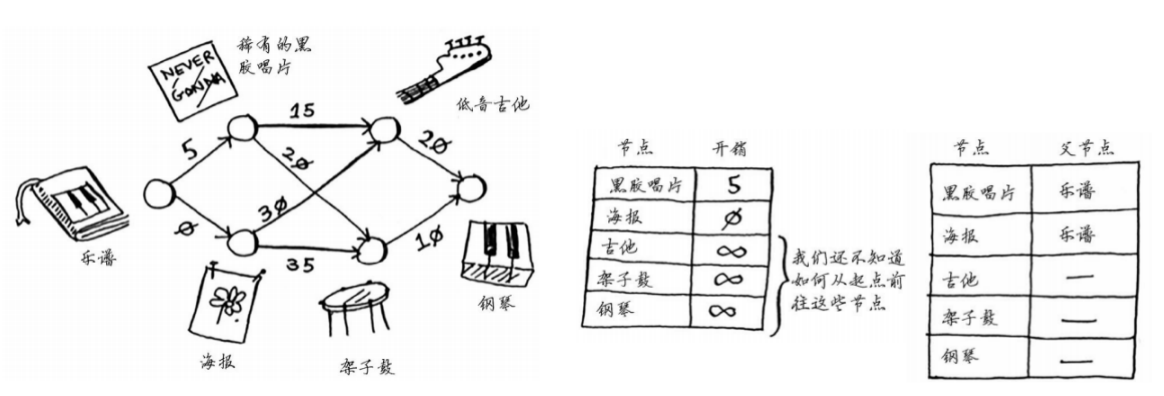
- 不同的同学手上有一些item
- 物品彼此之间可交换,可能需要添加费用
-
从某个同学出发,如何最少的费用换取其他心仪的物品?
- 准备:
- 构建图
- 创建节点开销表格,用于存储到每个节点的最小距离,会不断更新
-
创建父节点表格,用于最后追溯出具体的最短路径
-
一次寻找最便宜节点,更新其邻居节点
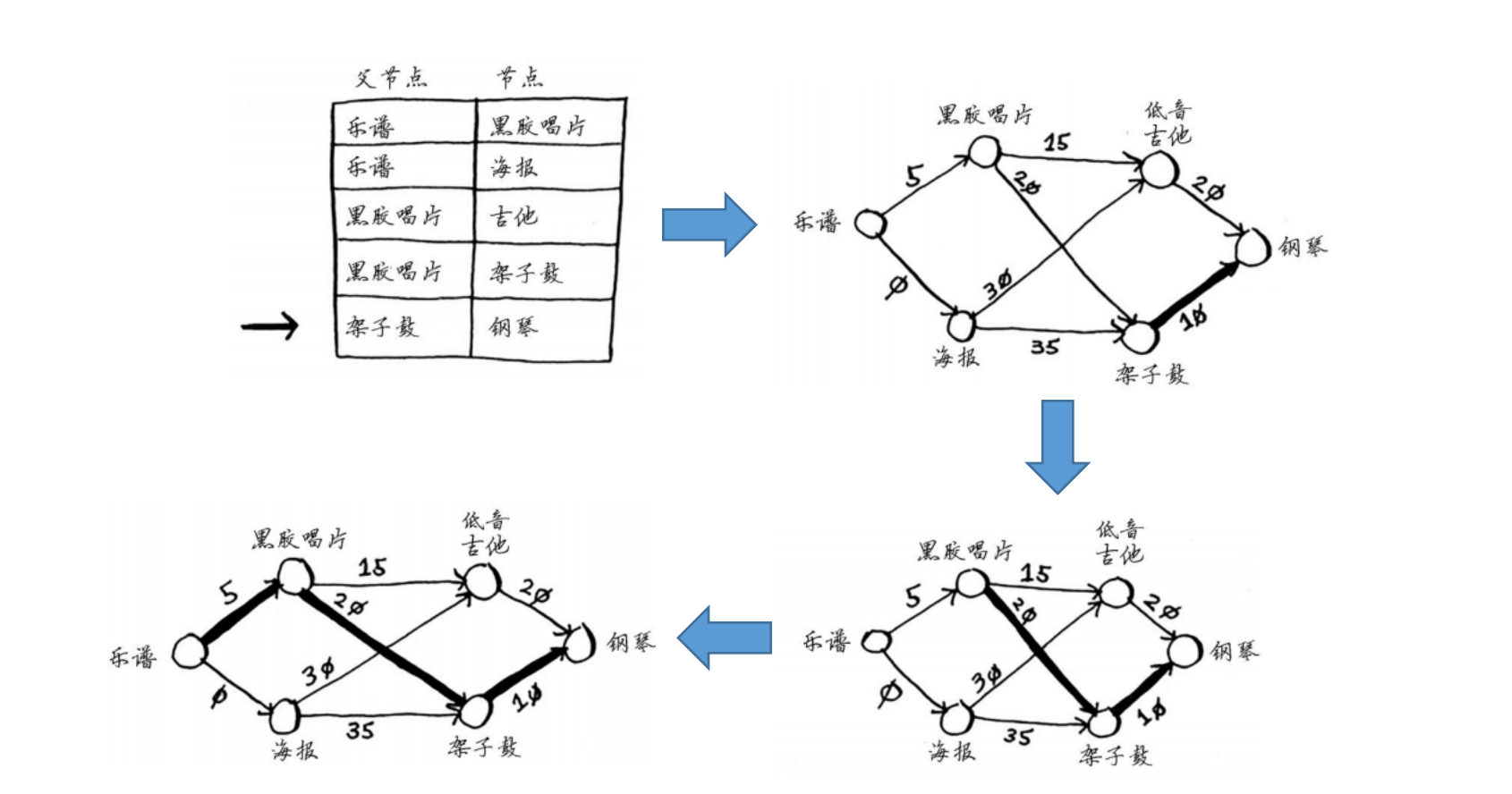
- 根据父节点表格回溯出最短路径
负权重
- 下面是个例子:
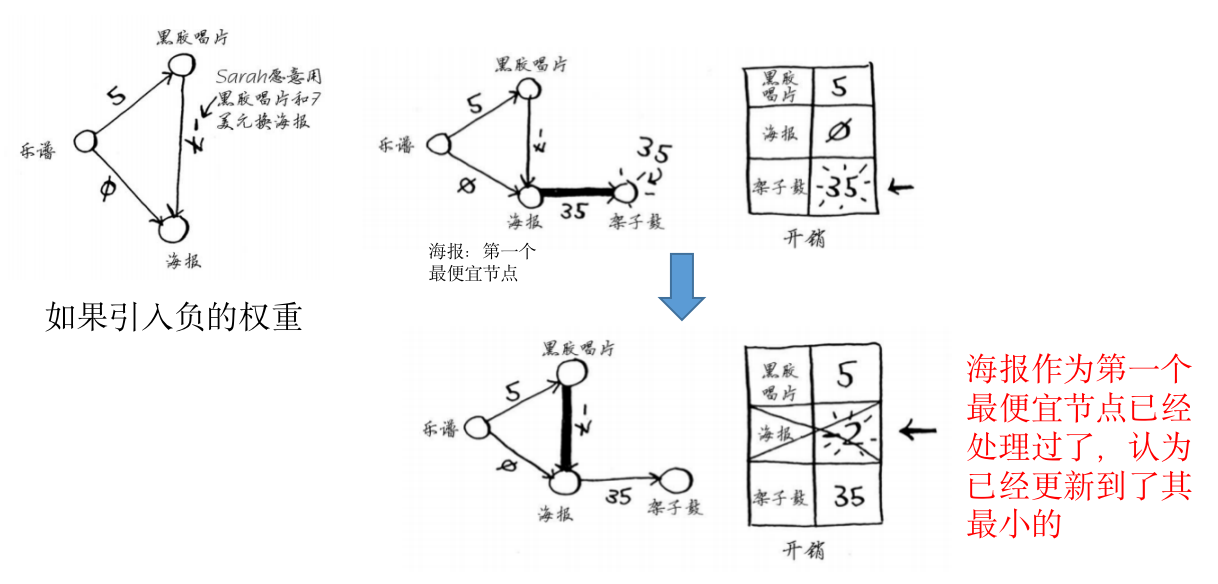
- 狄克斯特拉算法:
- 假设:对于处理过的节点(之前的最便宜的节点),没有前往该节点的更短路径
- 假设成立条件:在没有负权重时才成立
- 另一种算法:贝尔曼-福德算法,Bellman-Ford algorithm
实现
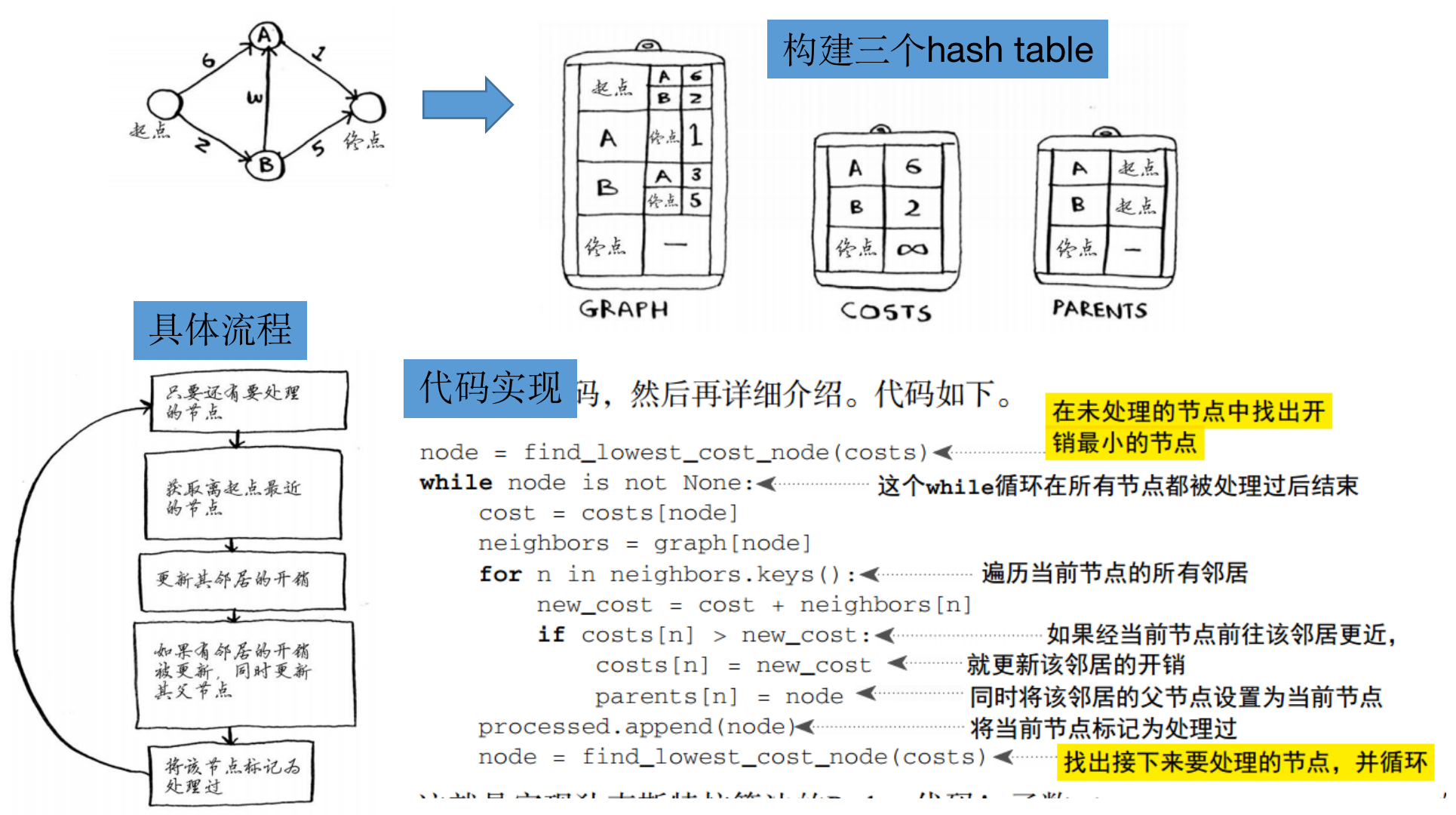
# the graph
graph = {}
graph["start"] = {}
graph["start"]["a"] = 6
graph["start"]["b"] = 2
graph["a"] = {}
graph["a"]["fin"] = 1
graph["b"] = {}
graph["b"]["a"] = 3
graph["b"]["fin"] = 5
graph["fin"] = {}
# the costs table
infinity = float("inf")
costs = {}
costs["a"] = 6
costs["b"] = 2
costs["fin"] = infinity
# the parents table
parents = {}
parents["a"] = "start"
parents["b"] = "start"
parents["fin"] = None
processed = []
def find_lowest_cost_node(costs):
lowest_cost = float("inf")
lowest_cost_node = None
# Go through each node.
for node in costs:
cost = costs[node]
# If it's the lowest cost so far and hasn't been processed yet...
if cost < lowest_cost and node not in processed:
# ... set it as the new lowest-cost node.
lowest_cost = cost
lowest_cost_node = node
return lowest_cost_node
# Find the lowest-cost node that you haven't processed yet.
node = find_lowest_cost_node(costs)
# If you've processed all the nodes, this while loop is done.
while node is not None:
cost = costs[node]
# Go through all the neighbors of this node.
neighbors = graph[node]
for n in neighbors.keys():
new_cost = cost + neighbors[n]
# If it's cheaper to get to this neighbor by going through this node...
if costs[n] > new_cost:
# ... update the cost for this node.
costs[n] = new_cost
# This node becomes the new parent for this neighbor.
parents[n] = node
# Mark the node as processed.
processed.append(node)
# Find the next node to process, and loop.
node = find_lowest_cost_node(costs)
print("Cost from the start to each node:")
print(costs)
参考
If you link this blog, please refer to this page, thanks!
Post link:https://tsinghua-gongjing.github.io/posts/algorithm-Dijkstra.html
Previous:
Algorithm: 图及图搜索
Next:
Algorithm: 近似算法中的贪婪算法
Latest articles
Links
- ZhangLab , RISE database , THU life , THU info
- Data analysis: pandas , numpy , scipy
- ML/DL: sklearn , sklearn(中文) , pytorch
- Visualization: seaborn , matplotlib , gallery
- Github: me