分治法
- divide & conquer
- 一种著名的递归式问题解决方法
- 不是一种具体的算法,而是一种思路
- 原理:
- (1)找出简单的基线条件
- (2)确定如何缩小问题的规模,使其符合基线条件
农场问题
- 描述:将一块土地均匀的分成方块,且分出的方块要尽可能大(因为理论上可以分成长度为1的方块)。
- 下面是三种切法:
- 第一个不是方块,不满足
- 第二个都是相同大小的方块,但是数目太多
- 第三个都是方块,但是大小不同,不满足

- 解法策略:
- 可采用分治法的策略
- 第一步:找到基线条件,需尽可能简单。
- 第二步:不断将问题分解,直到符合基线条件。
- 具体实现:
- 基线:如果一个方块的长边L1是短边L2的整数倍,那么这个方块能切分成L1/L2个短边方块,从而无需再继续切分,且此时所用的方块数目也是最少的。

- 切分流程示意:

- 基线:如果一个方块的长边L1是短边L2的整数倍,那么这个方块能切分成L1/L2个短边方块,从而无需再继续切分,且此时所用的方块数目也是最少的。
数组求和
- 描述:给定一个数组,返回数组的和
- 解法1:循环
- 循环数组,不断加和
def sum(arr):
total = 0
for x in arr:
total += x
return total
print(sum([1, 2, 3, 4]))
- 解法2:递归
- (1)找基线条件。
- 当数组为空时,元素和为0
- 当数组仅1个元素时,元素和为第一个元素
- (2)递归调用,缩小数组规模

- (1)找基线条件。
def sum(list):
if list == []:
return 0
return list[0] + sum(list[1:])
- 注意:
- 涉及数组的递归函数,基线条件通常是:数组为空或者只包含一个元素
- 当陷入困境时,请检查基线条件是不是这样的
快速排序
- 常用的排序算法
- 比选择排序快很多
- 采用了分治策略
- 解法:
- (1)基线条件:当数组为空或者只有1个元素时,无需排序,直接返回
- (2)不满足基线条件的,不断缩小规模进行递归调用进行排序
- 实现:
- (1)选择基准值(pivot):从数组中选择1个元素
- (2)分区(partioning):以基准值为阈值,找出比其小和大的值
- 小于基准值的子数组
- 基准值
- 大于基准值的子数组
- (3)排序:对两个子数组进行快速排序
- 例子:

def quicksort(array):
if len(array) < 2:
# base case, arrays with 0 or 1 element are already "sorted"
return array
else:
# recursive case
pivot = array[0]
# sub-array of all the elements less than the pivot
less = [i for i in array[1:] if i <= pivot]
# sub-array of all the elements greater than the pivot
greater = [i for i in array[1:] if i > pivot]
return quicksort(less) + [pivot] + quicksort(greater)
print(quicksort([10, 5, 2, 3]))
大O表示法
- 常见的大O运行时间对比
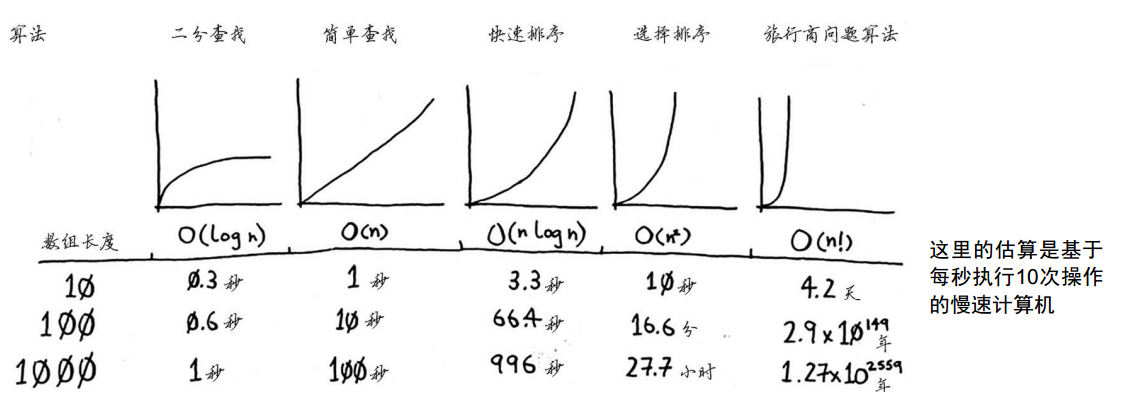
- 算法忽略了固定的时间量:
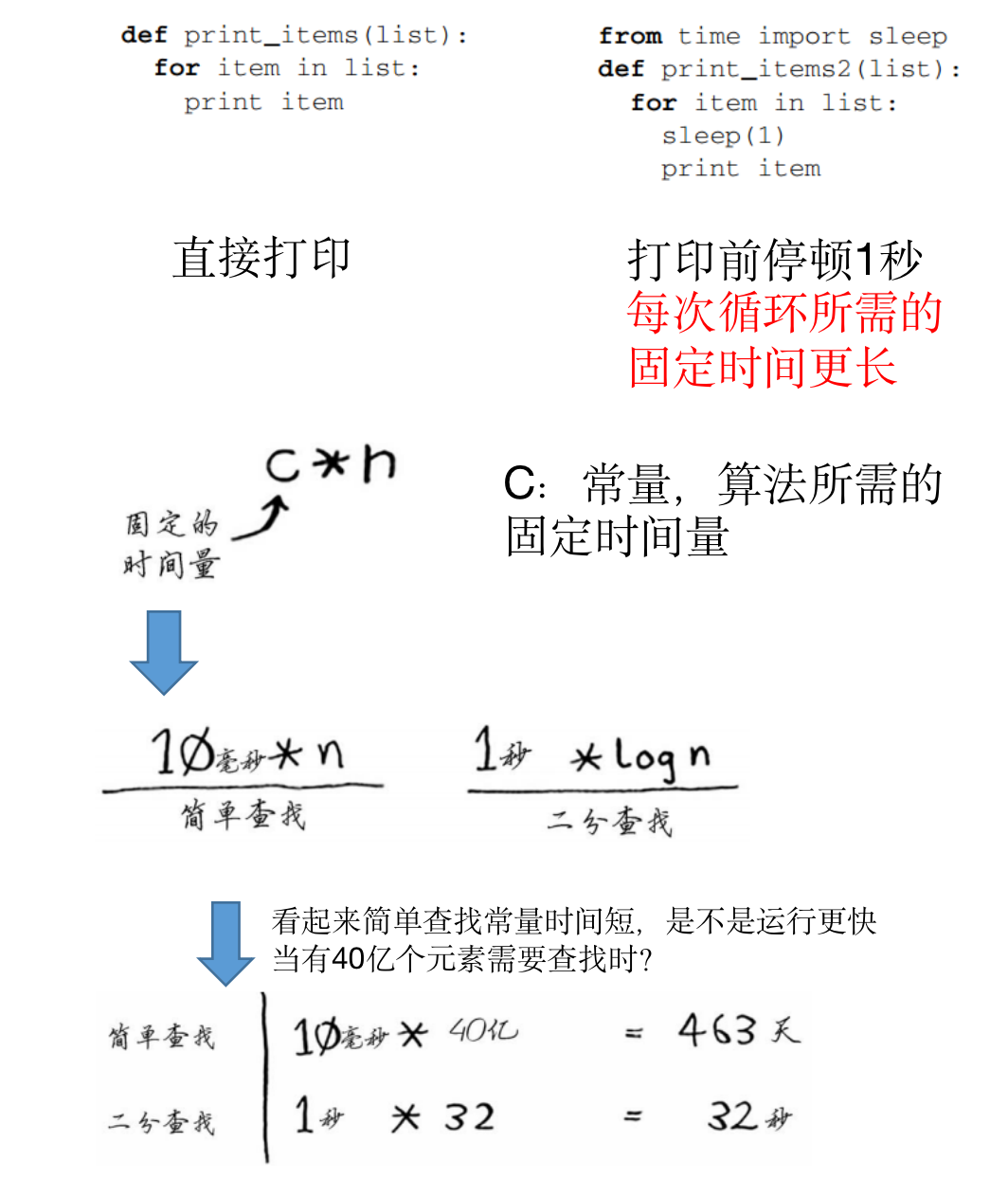
- 注意:
- 快排和合并排序的平均时间都是O(nlog n),但是前者的常量时间更短,所以速度是更快的
- 在简单查找和二分查找,常量几乎无关紧要,因为列表很长
- 平均情况和最糟情况:最佳情况也是平均情况,建议每次随机的选择一个元素作为基准值
- 快速排序:高度依赖于选择的基准值
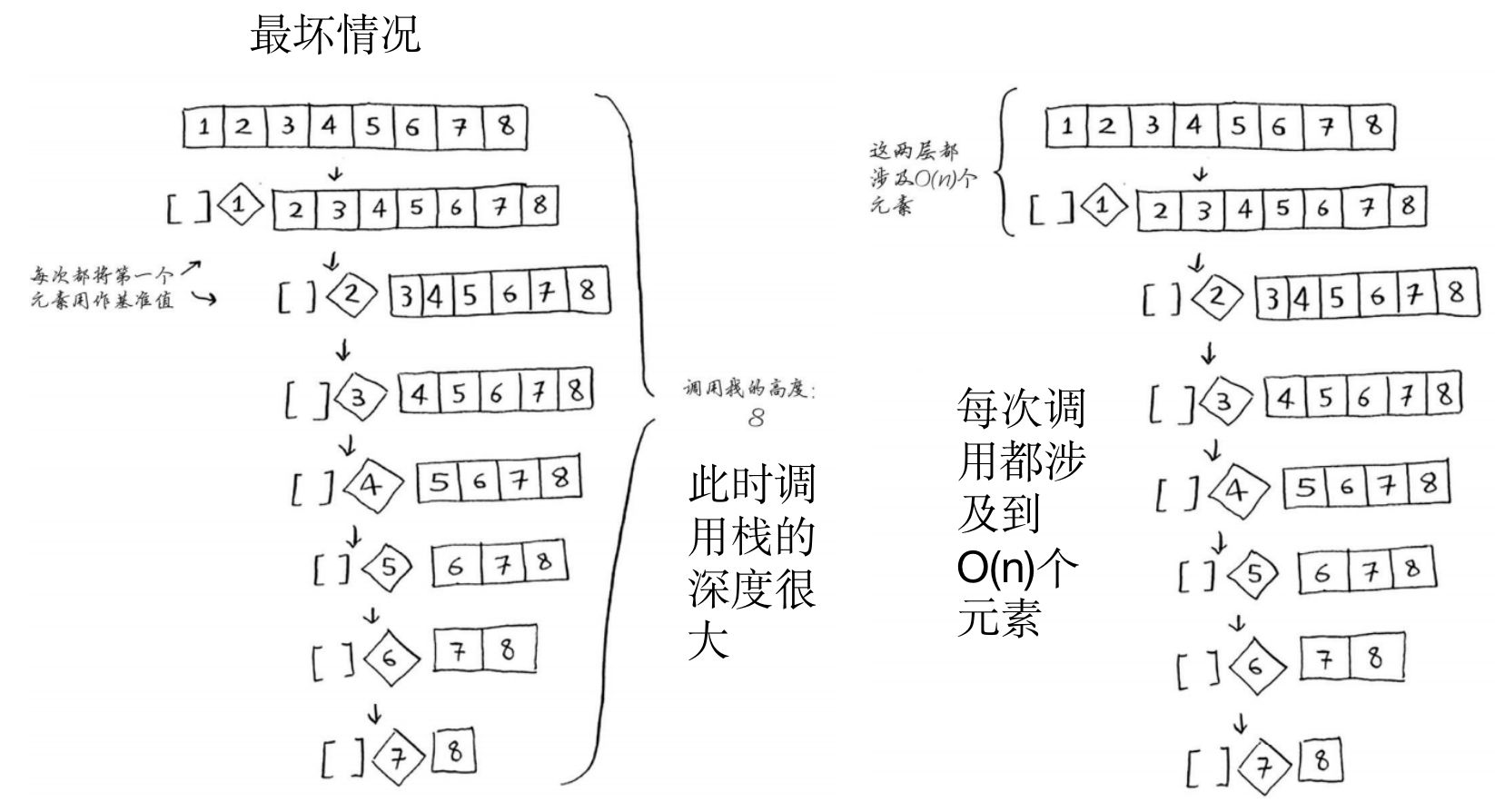
- 例子:对一个有序的数组进行排序
- 最坏情况:此时栈长为O(n)
- 最好情况:此时栈长为O(log n)
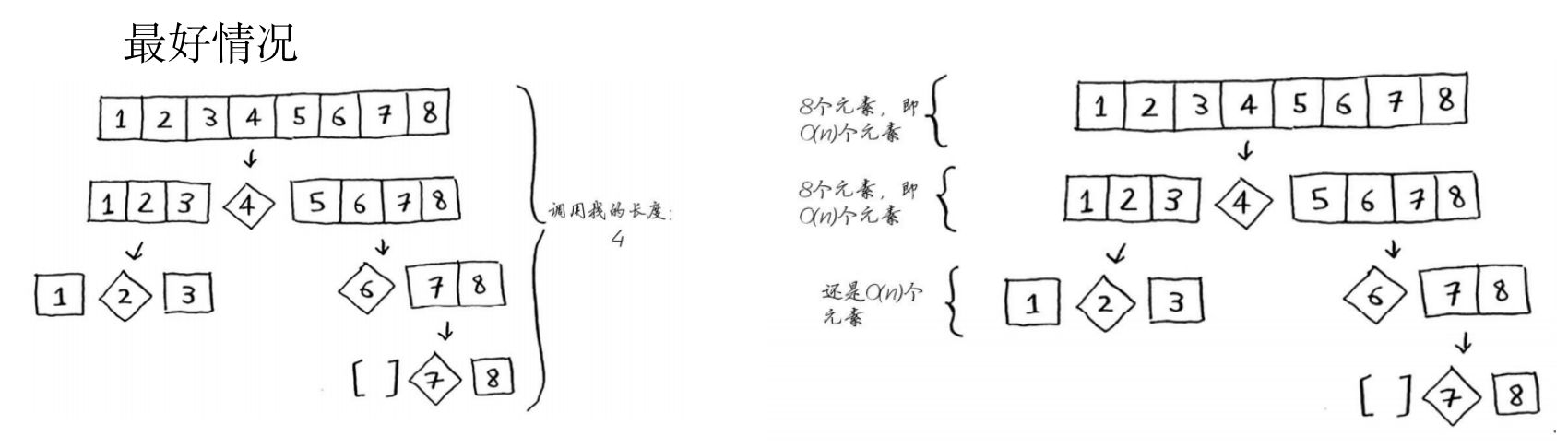
- 最坏情况:此时栈长为O(n)
参考
If you link this blog, please refer to this page, thanks!
Post link:https://tsinghua-gongjing.github.io/posts/algorithm-quick-sort.html
Previous:
Python module seaborn
Next:
Algorithm: 散列表(hash)
Latest articles
Links
- ZhangLab , RISE database , THU life , THU info
- Data analysis: pandas , numpy , scipy
- ML/DL: sklearn , sklearn(中文) , pytorch
- Visualization: seaborn , matplotlib , gallery
- Github: me