- 1. Python plot
- Set x axis tick labels
- Rotate x tick labels with axis
- Rotate x tick labels in seaborn
- Time series line plot
- Remove legend (also work in seaborn)
- Plot ax legend out of graph stackoverflow
- Set equal axis and x_lim/ylim github: set_ylim not working with plt.axis(‘equal’)
- Add y=x without tracking the data points stackoverflow
- Remove spines on the right and top
- Annotate point/position with non-overlapped text
- Add horizontal or vertical lines
- Add span regions stackoverflow
- Insert image file into axis stackoverflow
- Save multiple plot into a pdf discuss here
- add annotations
- add statistical test p-value
- joint reg plot with R/p-value
- set ylabel on the right
- 画双y轴的图
- 2. Seaborn plot
- 3. Inkscape
- 4. MagicImage
1. Python plot
Set x axis tick labels
# assign tick position and label
# especially for bar plot or time series plot
plt.xticks(range(0, len(compare_cell_ls)), compare_cell_ls, rotation=45)
# Not work: label will off-set 1 (still don't know why)
ax.set_xticklabels(compare_cell_ls, rotation=45)
Rotate x tick labels with axis
# auto get & rotate
ax[0].set_xticklabels(ax[0].xaxis.get_majorticklabels(), rotation=45)
Rotate x tick labels in seaborn
# work for last row graph, not Every plots (in FacetGrid)
g.set_xticklabels(rotation=45)
Time series line plot
# data format
# each row denote a gene's expression under different condition
[zhangqf7@loginview02 HuR]$ head predict_RBP_binding_combine.compare.txt|cut -f 4-7
egg 1cell 4cell 64cell
0.21742857142857144 0.34700000000000003 0.12 0.13285714285714287
0.22228571428571428 0.1551428571428571 0.03528571428571429 0.04671428571428572
0.12285714285714285 0.07571428571428572 0.027000000000000003 0.026857142857142857
0.41571428571428576 0.5638571428571428 0.34114285714285714 0.2785714285714286
0.4587142857142856 0.3832857142857143 0.40771428571428575 0.3097142857142857
0.217 0.2868571428571429 0.13699999999999998 0.14914285714285716
0.21757142857142855 0.4165714285714285 0.1558571428571429 0.15371428571428572
0.33399999999999996 0.3514285714285714 0.1827142857142857 0.17557142857142854
0.32557142857142857 0.3127142857142857 0.19657142857142856 0.2992857142857143
# plot each as trend line
fig,ax=plt.subplots()
for i in df_plot.index:
ax.plot(range(0, len(col_ls)), df_plot.loc[i, col_ls], color='grey', alpha=0.3, lw=0.3)
# mean value of each state
# axis=0 => mean of each column (add a new row); axis=1 => mean of each row (add a new column)
df_plot_mean = df_plot.loc[:, compare_cell_ls].mean(axis=0)
ax.plot(range(0, len(compare_cell_ls)), df_plot_mean, color='blue')
Remove legend (also work in seaborn)
ax.legend_.remove()
# show legend
plt.legend()
Plot ax legend out of graph stackoverflow
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(10)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.subplot(111)
for i in xrange(5):
ax.plot(x, i * x, label='$y = %ix$'%i)
# Shrink current axis by 20%
box = ax.get_position()
ax.set_position([box.x0, box.y0, box.width * 0.8, box.height])
# Put a legend to the right of the current axis
ax.legend(loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(1, 0.5))
plt.show()
# Use plot with tight mode, or plot will be cut
plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1, 1), loc=2)
plt.savefig(savefn, bbox_inches='tight')

Set equal axis and x_lim/ylim github: set_ylim not working with plt.axis(‘equal’)
plt.plot((.1, .3))
ax.axis('square')
ax.set_xlim(0.1, 0.3)
# in seaborn like jointplot also works
g = sns.jointplot(x='col1', y='col2', data=d_g, kind="reg", stat_func=stats.pearsonr, size=10)
g.ax_joint.set_xlim(0.35, 0.9)
g.ax_joint.set_ylim(0.35, 0.9)
Add y=x without tracking the data points stackoverflow
lims = [
np.min([ax.get_xlim(), ax.get_ylim()]), # min of both axes
np.max([ax.get_xlim(), ax.get_ylim()]), # max of both axes
]
# now plot both limits against eachother
ax.plot(lims, lims, 'k-', alpha=0.75, zorder=0)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.set_xlim(lims)
ax.set_ylim(lims)

Remove spines on the right and top
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
Annotate point/position with non-overlapped text
Use ax.annotate() as stackoverflow, can ass marks like arrow etc.:
y = [2.56422, 3.77284, 3.52623, 3.51468, 3.02199]
z = [0.15, 0.3, 0.45, 0.6, 0.75]
n = [58, 651, 393, 203, 123]
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(z, y)
for i, txt in enumerate(n):
ax.annotate(txt, (z[i], y[i]))
Can also use plt.text() function:
# with x,y denote absolute coordinates
plt.text(x, y, s, fontsize=12)
# with transform to project the axes
# 这里的x,y就是相对于坐标轴的哪个位置的
plt.text(0.5, 0.5, str, ha='center',va='center', transform=ax.transAxes)
Non-overlapped text based on module adjustText as example here:
# here is a very useful library to adjust overlapped text
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/19073683/matplotlib-overlapping-annotations-text
# https://github.com/Phlya/adjustText
from adjustText import adjust_text
texts = []
for x, y, s in zip(xs, ys, ss):
texts.append(plt.text(x, y, s))
adjust_text(texts, only_move={'text': 'y'})
Add horizontal or vertical lines
# 这个是画水平或者竖直的线,只指定x或者y时,跨越坐标轴
# 指定比如xmin/xmax时,画对应的比例。这些值取值为[0,1]之间
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/16930328/vertical-horizontal-lines-in-matplotlib/16930526
plt.axhline(y=0, xmin=0, xmax=1, hold=None, **kwargs)
plt.axvline(x=0, ymin=0, ymax=1, hold=None, **kwargs)
# 直接连接任意两点,指定两点的坐标时
plt.plot((x1, x2), (y1, y2), 'k-')
Add span regions stackoverflow
plt.axvspan(3, 6, color='red', alpha=0.5)
Insert image file into axis stackoverflow
im = plt.imread('grace_hopper.jpg')
newax = fig.add_axes([0.8, 0.8, 0.2, 0.2], anchor='NE', zorder=-1)
newax.imshow(im)
newax.axis('off')
Save multiple plot into a pdf discuss here
比如下面的代码,可以把多个iteration的训练过程的loss和accuracy画在一个pdf文件中:
from matplotlib.backends.backend_pdf import PdfPages
def plot_history(history, pdf):
fig,ax = plt.subplots()
# Plot training & validation accuracy values
plt.plot(history['acc'])
plt.plot(history['val_acc'])
plt.title('Model accuracy')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.legend(['Train', 'Test'], loc='upper left')
pdf.savefig(fig)
fig,ax = plt.subplots()
# Plot training & validation loss values
plt.plot(history['loss'])
plt.plot(history['val_loss'])
plt.title('Model loss')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.legend(['Train', 'Test'], loc='upper left')
pdf.savefig(fig)
pdf = matplotlib.backends.backend_pdf.PdfPages(plot_savefn)
for ite in range(n_ite):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data, labels, test_size=0.4,)
clf.fit(X_train)
history = clf.history_
plot_history(history, pdf)
plt.close()
pdf.close()
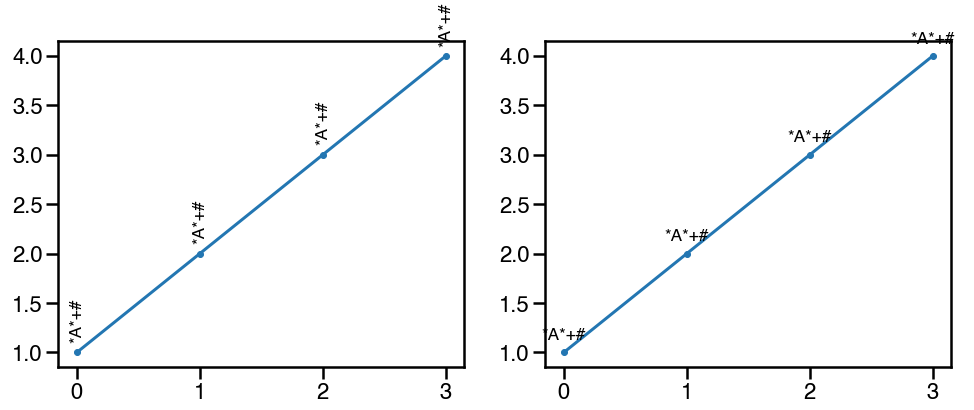
add annotations
可以使用ax.text函数,在特定的位置添加注释。一个常用的场景是标注显著性,比如pvalue<=0.01的标注为**,但是需要注意的是,如果旋转为垂直方向,**通常是不会和其提供的x坐标位置对齐,因为*本身是不和字母对齐的,这个时候可以选用其他的字符,比如+#等:
d1 = pd.DataFrame({'0':[1,2,3,4], '1':[4,5,6,5]})
fig,ax=plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(16,6))
ax[0].plot(d1['0'], marker='.')
for n,i in enumerate(d1['0']):
ax[0].text(n, i+0.1, '*A*+#', va='bottom', ha='center', rotation='vertical', size='xx-large')
ax[1].plot(d1['0'], marker='.')
for n,i in enumerate(d1['0']):
ax[1].text(n, i+0.1, '*A*+#', va='bottom', ha='center', rotation=0, size='xx-large')
add statistical test p-value
As discussed here:
Based on manual setup:
import seaborn as sns, matplotlib.pyplot as plt
tips = sns.load_dataset("tips")
sns.boxplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips, palette="PRGn")
# statistical annotation
x1, x2 = 2, 3 # columns 'Sat' and 'Sun' (first column: 0, see plt.xticks())
y, h, col = tips['total_bill'].max() + 2, 2, 'k'
plt.plot([x1, x1, x2, x2], [y, y+h, y+h, y], lw=1.5, c=col)
plt.text((x1+x2)*.5, y+h, "ns", ha='center', va='bottom', color=col)
plt.show()

Based on repo statannot, which works for seaborn boxplot only:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from statannot import add_stat_annotation
sns.set(style="whitegrid")
df = sns.load_dataset("tips")
x = "day"
y = "total_bill"
order = ['Sun', 'Thur', 'Fri', 'Sat']
ax = sns.boxplot(data=df, x=x, y=y, order=order)
add_stat_annotation(ax, data=df, x=x, y=y, order=order,
boxPairList=[("Thur", "Fri"), ("Thur", "Sat"), ("Fri", "Sun")],
test='Mann-Whitney', textFormat='star', loc='outside', verbose=2)

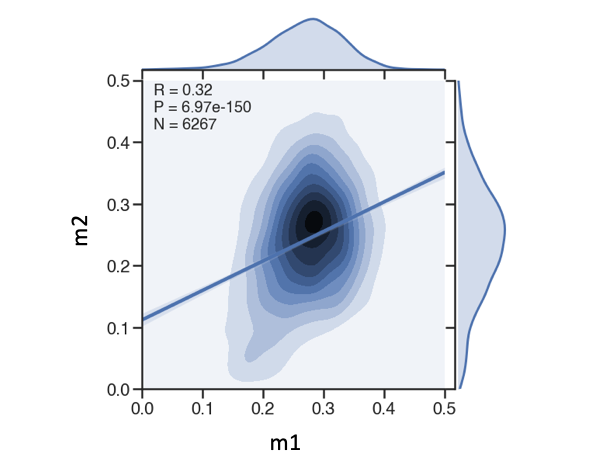
joint reg plot with R/p-value
g = sns.jointplot(x='m1',y='m2',data=df,kind='kde', xlim=(0.0,0.5), ylim=(0.0,0.5), height=8, ratio=5)
sns.regplot(df['m1'],df['m2'], scatter=False, ax=g.ax_joint)
r,p = stats.pearsonr(df['m1'],df['m2'])
s = 'R = {:.2f}\nP = {:.2e}\nN = {}'.format(r,p,df.shape[0])
g.ax_joint.text(0.05, 0.9, s, ha='left', va='top', size=20, transform=g.ax_joint.transAxes)
set ylabel on the right
参考这里
ax.yaxis.set_label_position("right")
ax.yaxis.tick_right()
画双y轴的图
官网例子:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Create some mock data
t = np.arange(0.01, 10.0, 0.01)
data1 = np.exp(t)
data2 = np.sin(2 * np.pi * t)
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots()
color = 'tab:red'
ax1.set_xlabel('time (s)')
ax1.set_ylabel('exp', color=color)
ax1.plot(t, data1, color=color)
ax1.tick_params(axis='y', labelcolor=color)
ax2 = ax1.twinx() # instantiate a second axes that shares the same x-axis
color = 'tab:blue'
ax2.set_ylabel('sin', color=color) # we already handled the x-label with ax1
ax2.plot(t, data2, color=color)
ax2.tick_params(axis='y', labelcolor=color)
fig.tight_layout() # otherwise the right y-label is slightly clipped
plt.show()
2. Seaborn plot
Set color list instead of seaborn default
# get python default color list
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/42086276/get-default-line-colour-cycle
# color_ls = plt.rcParams['axes.prop_cycle'].by_key()['color']
# seaborn color list
color_stages = sns.color_palette('Set1',n_colors=7, desat=0.8)
my_pal = {'egg':color_stages[0], '1cell': color_stages[1], '4cell': color_stages[2], '64cell': color_stages[3], '1K': color_stages[4], 'sphere':color_stages[5], 'shield':color_stages[6]}
Set specific color for different category using dict
sns.boxplot(x='cell', y='gini', data=df_save_all, ax=ax[0], palette=file_info_dict['my_pal'])
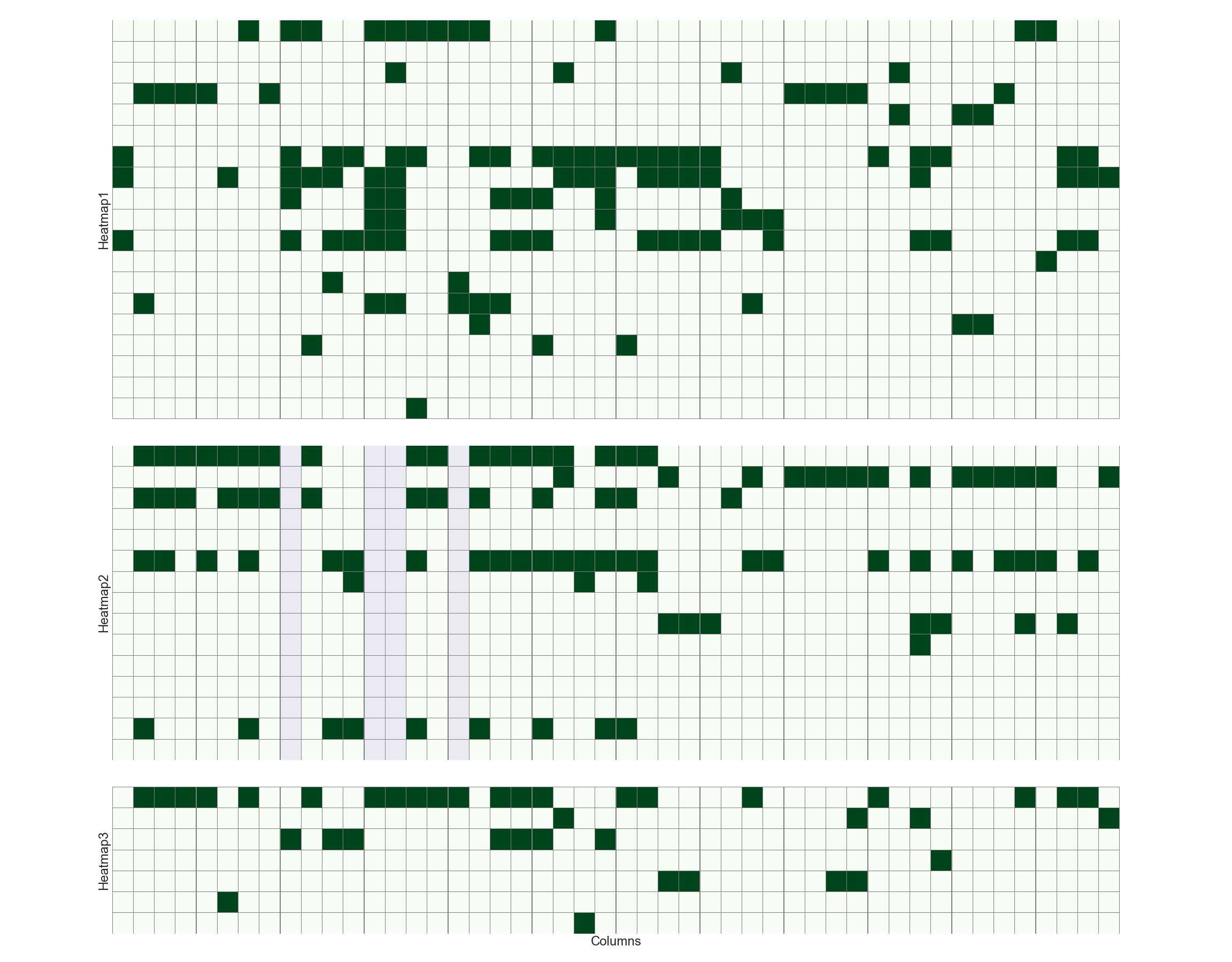
Plot multiple heatmap with subplots
### 指定height_ratios,一般根据每个集合具有的feature的数目
fig, ax = plt.subplots(3,1,figsize=(32, 25), gridspec_kw = {'height_ratios':[19, 15, 7]}, sharey=False, sharex=True)
### plot heatmap
h1 = sns.heatmap(df_plot_all[function_ls[1:]].T,linecolor='grey', linewidths=0.1, cbar=False, square=True, cmap="Greens", ax=ax[0])
h2 = sns.heatmap(df_plot_all[localization_ls].T,linecolor='grey', linewidths=0.1, cbar=False, square=True, cmap="Greens", ax=ax[1])
h3 = sns.heatmap(df_plot_all[domain_ls].T,linecolor='grey', linewidths=0.1, cbar=False, square=True, cmap="Greens", ax=ax[2])
### keep one xlabel for all, also keep yticklabels
# h1.set(xlabel='', ylabel='Heatmap1')
# h2.set(xlabel='', ylabel='Heatmap2')
# h3.set(xlabel='Columns', ylabel='Heatmap3')
### keep one xlabel for all, remove yticklabels
h1.set(xlabel='', ylabel='Heatmap1', yticks=[])
h2.set(xlabel='', ylabel='Heatmap2', yticks=[])
h3.set(xlabel='Columns', ylabel='Heatmap3', yticks=[], xticks=[])
### set yticklabels on the right
ax[0].yaxis.tick_right()
ax[0].set_yticklabels(ax[0].yaxis.get_majorticklabels(), rotation=0)
ax[1].yaxis.tick_right()
ax[1].set_yticklabels(ax[1].yaxis.get_majorticklabels(), rotation=0)
ax[2].yaxis.tick_right()
ax[2].set_yticklabels(ax[2].yaxis.get_majorticklabels(), rotation=0)
ax[2].set_xticklabels(ax[2].xaxis.get_majorticklabels(), rotation=90)
### set tick label color individually
### https://stackoverflow.com/questions/21936014/set-color-for-xticklabels-individually-in-matplotlib
# color_ls = ['red']*10+['black']*19
# [t.set_color(i) for (i,t) in zip(color_ls,ax[2].xaxis.get_ticklabels())]
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('./test.png')
plt.close()
Reverse y axis of heatmap
As discussed here
import numpy as np; np.random.seed(0)
import seaborn as sns; sns.set()
uniform_data = np.random.rand(10, 12)
ax = sns.heatmap(uniform_data)
ax.invert_yaxis()
change heatmap size
No size argument in sns.heatmap function, can only set by plt as discussed here
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 16))
sns.heatmap(..., ax=ax)
设置heatmap注释数值自字体大小
使用annot_kws字典参数,参考这里:
sns.heatmap(corrmat,
vmin=corrmat.values.min(),
vmax=1, square=True, cmap="YlGnBu",
linewidths=0.1, annot=True,
annot_kws={"fontsize":8})
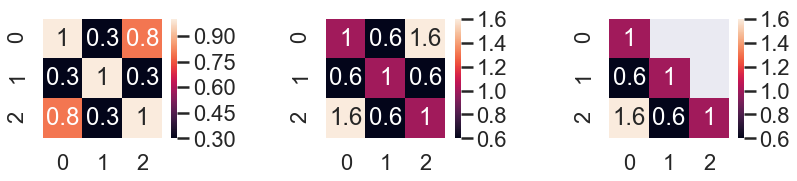
Merge symmetry matrix value to one side
def merge_symmetry_df_to_diagonal_lower(df=None):
if df is None:
df = pd.DataFrame({0:[1, 0.3, 0.8], 1:[0.3, 1, 0.3], 2:[0.8, 0.3, 1]})
df_twice = df + df.T
# df_twice.values[[np.arange(df.shape[0])]*2] = df_twice.values[[np.arange(df.shape[0])]*2] / 2
df_twice.values[[np.arange(df.shape[0])]*2] = np.diagonal(df)
return df_twice
d1 = pd.DataFrame({0:[1, 0.3, 0.8], 1:[0.3, 1, 0.3], 2:[0.8, 0.3, 1]})
d = merge_symmetry_df_to_diagonal_lower()
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,3, figsize=(12,3))
sns.heatmap(d1, ax=ax[0], square=True, annot=True)
sns.heatmap(d, ax=ax[1], square=True, annot=True)
mask = np.zeros_like(d)
mask[np.triu_indices_from(mask)] = True
mask[np.diag_indices_from(mask)] = False
sns.heatmap(d, ax=ax[2], square=True, annot=True, mask=mask)
plt.tight_layout()
Change NULL value color in heatmap
参考这里直接设置背景颜色即可:
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(10,20))
g = sns.heatmap(df_3, xticklabels=False, yticklabels=False, cmap="summer")
g.set_facecolor('black')
3. Inkscape
Convert pdf to svg (stackoverflow), only for first page
/Applications/Inkscape.app/Contents/Resources/bin/inkscape -l Python_graph.svg Python_graph.pdf
4. MagicImage
Combine multiple image into one figure/pdf file
# auto rows and columns
montage *png out.pdf
# use filename to label each image
montage -label '%f' * out.pdf
# 4 columns x multiple rows
montage *.png -mode concatenate -tile 4x out.pdf
merge multiple .pdf into one
# by default: one pdf per page
convert *pdf merge.pdf
# 和合并图片一样,可以指定行列数(-tile)
montage *pdf -mode concatenate merge.pdf
If you link this blog, please refer to this page, thanks!
Post link:https://tsinghua-gongjing.github.io/posts/python-plot-tricks.html
Previous:
Visualization network using Cytoscape tools
Next:
Seaborn plot collections
Latest articles
Links
- ZhangLab , RISE database , THU life , THU info
- Data analysis: pandas , numpy , scipy
- ML/DL: sklearn , sklearn(中文) , pytorch
- Visualization: seaborn , matplotlib , gallery
- Github: me