- Calculate distance between two intervals stackoverflow
- Sort a column by specific order in a df stackoverflow
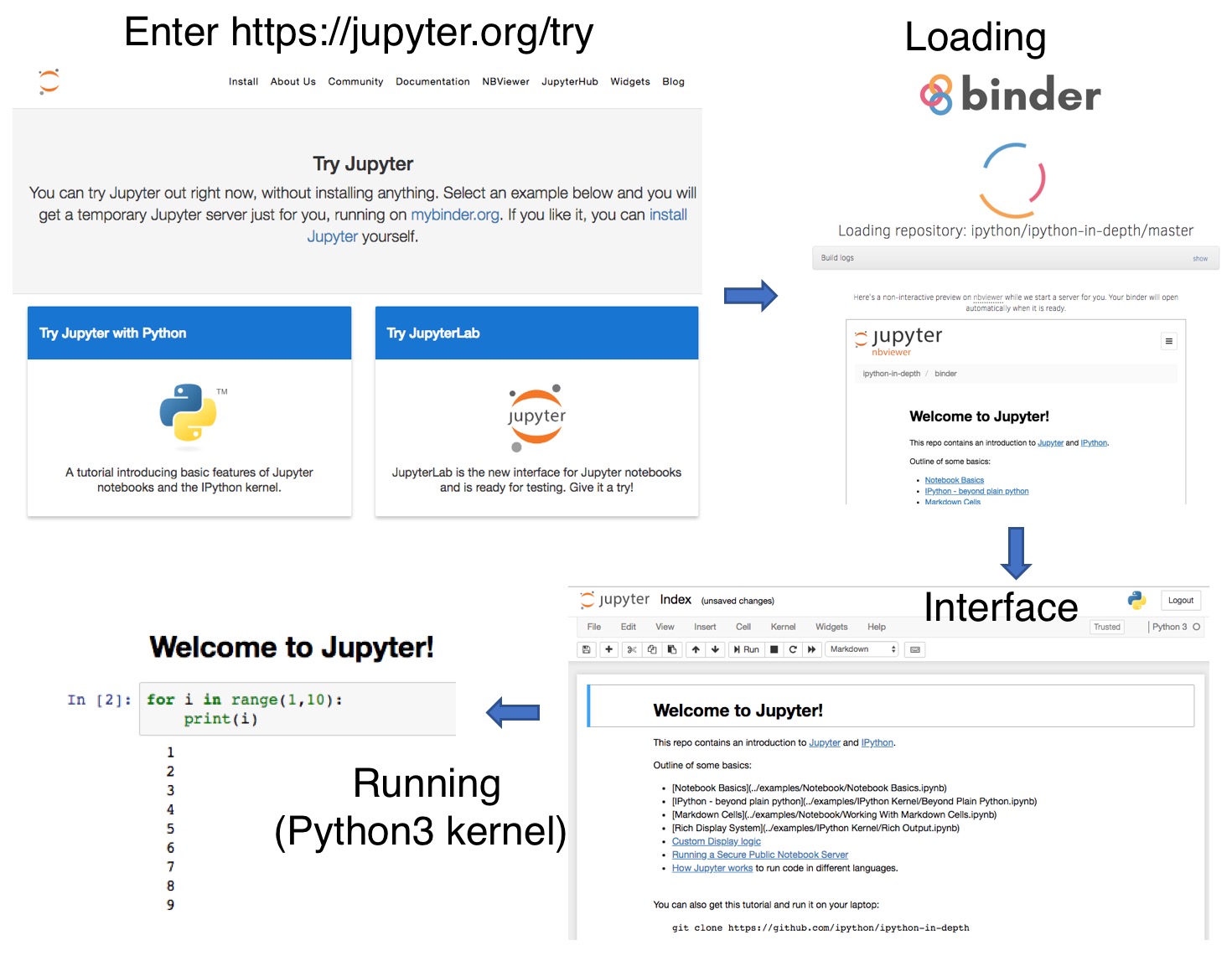
- Free online jupyter
- Normalize data frame by row/column sum stackoverflow
- Write multiple df to one sheet with multiple tab stackoverflow
- 根据df某一列的值,找到其最大值所对应的index
- 设置画图时使用Helvetica字体
- 画图时支持中文
- 将array里面的NA值替换为其他实数值
- 核查文件夹是否存在否则创建
- 把df中的某一列按照特定字符分隔成多列
- 在
df中使用cut进行分bin,获得对应的bin值 - 更改pip安装包的源
- 获取一列数对应的排序
- 计算df中每一列的缺失值比例
- 在jupyter中使用运行时间
- df中分组,将某一列合并为一行
- 对于数组计算累计值
- 对于df指定列,找出最接近某个输入值的行
- 使用模块管理工具
importlib - 对df中缺失值进行填充
- csv写文件时全为逗号隔开的
- 设置
.pythonrc文件在打开python console时自动执行
Calculate distance between two intervals stackoverflow
def solve(r1, r2):
# sort the two ranges such that the range with smaller first element
# is assigned to x and the bigger one is assigned to y
x, y = sorted((r1, r2))
#now if x[1] lies between x[0] and y[0](x[1] != y[0] but can be equal to x[0])
#then the ranges are not overlapping and return the differnce of y[0] and x[1]
#otherwise return 0
if x[0] <= x[1] < y[0] and all( y[0] <= y[1] for y in (r1,r2)):
return y[0] - x[1]
return 0
...
>>> solve([0,10],[12,20])
2
>>> solve([5,10],[1,5])
0
>>> solve([5,10],[1,4])
1
Sort a column by specific order in a df stackoverflow
# the specific order
sorter = ['a', 'c', 'b']
df['column'] = df['column'].astype("category")
df['column'].cat.set_categories(sorter, inplace=True)
df.sort_values(["column"], inplace=True)
Free online jupyter
A free Python/R notebook can also be created online at https://rdrr.io/.
Normalize data frame by row/column sum stackoverflow
t = pd.DataFrame({1:[1,2,3], 2:[3,4,5], 3:[6,7,8]})
t
1 2 3
0 1 3 6
1 2 4 7
2 3 5 8
# by row sum
t.div(t.sum(axis=1), axis=0)
1 2 3
0 0.100000 0.300000 0.600000
1 0.153846 0.307692 0.538462
2 0.187500 0.312500 0.500000
# by column sum
t.div(t.sum(axis=0), axis=1)
1 2 3
0 0.166667 0.250000 0.285714
1 0.333333 0.333333 0.333333
2 0.500000 0.416667 0.380952
Write multiple df to one sheet with multiple tab stackoverflow
def dfs_tabs(df_list, sheet_list, file_name):
writer = pd.ExcelWriter(file_name,engine='xlsxwriter')
for dataframe, sheet in zip(df_list, sheet_list):
dataframe.to_excel(writer, sheet_name=sheet, startrow=0 , startcol=0, index=False)
writer.save()
根据df某一列的值,找到其最大值所对应的index
As discussed here:
df = pd.DataFrame({'favcount':[1,2,3], 'sn':['a','b','c']})
print (df)
favcount sn
0 1 a
1 2 b
2 3 c
print (df.favcount.idxmax())
2
print (df.ix[df.favcount.idxmax()])
favcount 3
sn c
Name: 2, dtype: object
print (df.ix[df.favcount.idxmax(), 'sn'])
c
设置画图时使用Helvetica字体
主要参考这篇文章:Changing the sans-serif font to Helvetica。转换好的字体文件放在了这里,可下载使用。
# 在mac上找到Helvetica字体
$ ls /System/Library/Fonts/Helvetica.ttc
# 复制到其他的位置
$ cp /System/Library/Fonts/Helvetica.ttc ~/Desktop
# 使用online的工具转换为.tff文件
# 这里使用的是: https://www.files-conversion.com/font/ttc
# 定位python库的字体文件
$ python -c 'import matplotlib ; print(matplotlib.matplotlib_fname())'
/Users/gongjing/usr/anaconda2/lib/python2.7/site-packages/matplotlib/mpl-data/matplotlibrc
# 将tff文件放到上述路径的font目录下
$ cp Helvetica.ttf /Users/gongjing/usr/anaconda2/lib/python2.7/site-packages/matplotlib/mpl-data/fonts/ttf
# 修改matplotlibrc文件
#font.sans-serif : DejaVu Sans, Bitstream Vera Sans, Computer Modern Sans Serif, Lucida Grande, Verdana, Geneva, Helvetica, Lucid, Arial, Avant Garde, sans-serif
=》font.sans-serif : Helvetica, DejaVu Sans, Bitstream Vera Sans, Computer Modern Sans Serif, Lucida Grande, Verdana, Geneva, Lucid, Arial, Avant Garde, sans-serif
# 重启jupyter即可
上面是设置全局的,也可以显示的在代码中指定,可以参考这里:
# 显示指定在此脚本中用某个字体
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "Helvetica"
# 对于不同的部分(标题、刻度等)指定不同的字体
csfont = {'fontname':'Comic Sans MS'}
hfont = {'fontname':'Helvetica'}
plt.title('title',**csfont)
plt.xlabel('xlabel', **hfont)
plt.show()
画图时支持中文
画图时,如果需要使用中文label,需要设置,主要参考这里:
- 1、下载
SimHei黑体字体文件 - 2、将下载的
.tff文件放到matplotlib包的路径下,路径为:matplotlib/mpl-data/fonts/ttf,可以使用pip show matplotlib查看包安装的位置 - 3、修改配置文件:
matplotlibrc,一般在matplotlib/mpl-data/这个下面。- font.family : sans-serif
- font.sans-serif : SimHei, Bitstream Vera Sans, Lucida Grande, Verdana, Geneva, Lucid, Arial, Helvetica, Avant Garde, sans-serif
- axes.unicode_minus:False
- 4、删除
/Users/gongjing/.matplotlib下面缓存的字体文件 - 5、再直接调用即可
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "SimHei"
将array里面的NA值替换为其他实数值
可以使用numpy的函数nan_to_num:numpy.nan_to_num(x, copy=True)]
x = np.array([np.inf, -np.inf, np.nan, -128, 128])
# 默认copy=True,不改变原来数组的值
np.nan_to_num(x)
array([ 1.79769313e+308, -1.79769313e+308, 0.00000000e+000,
-1.28000000e+002, 1.28000000e+002])
# 设置copy=False,原来数组的值会被替换
np.nan_to_num(x, copy=False)
核查文件夹是否存在否则创建
As discussed here:
import os
def check_dir_or_make(d):
if not os.path.exists(d):
os.makedirs(d)
把df中的某一列按照特定字符分隔成多列
As discussed here:
df = pd.DataFrame({'Name': ['Steve_Smith', 'Joe_Nadal',
'Roger_Federer'],
'Age':[32,34,36]})
# Age Name
# 0 32 Steve_Smith
# 1 34 Joe_Nadal
# 2 36 Roger_Federer
df[['First','Last']] = df.Name.str.split("_",expand=True,)
# expand需要设置为True,负责报错说原来df没有“first”,“last”列
# Age Name First Last
# 0 32 Steve_Smith Steve Smith
# 1 34 Joe_Nadal Joe Nadal
# 2 36 Roger_Federer Roger Federer
在df中使用cut进行分bin,获得对应的bin值
# 将数据分成10组
bins = 10
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict({'value':[i/10 for i in range(10+1)]})
df['bins'] = pd.cut(df['value'], bins=bins)
df
value bins
0 0.0 (-0.001, 0.1]
1 0.1 (-0.001, 0.1]
2 0.2 (0.1, 0.2]
3 0.3 (0.2, 0.3]
4 0.4 (0.3, 0.4]
5 0.5 (0.4, 0.5]
6 0.6 (0.5, 0.6]
7 0.7 (0.6, 0.7]
8 0.8 (0.7, 0.8]
9 0.9 (0.8, 0.9]
10 1.0 (0.9, 1.0]
# 通过以value_counts()的index获得唯一的bin
# 打印:此时每一个i是interval对象
for i in list(df['bins'].value_counts().index):
print(i)
(-0.001, 0.1]
(0.9, 1.0]
(0.8, 0.9]
(0.7, 0.8]
(0.6, 0.7]
(0.5, 0.6]
(0.4, 0.5]
(0.3, 0.4]
(0.2, 0.3]
(0.1, 0.2]
# interval对象不能通过index进行取值
i[0]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-46-3aa51af8ff05> in <module>()
----> 1 i[0]
TypeError: 'pandas._libs.interval.Interval' object does not support indexing
# interval对象有特定的属性进行取值等操作
# closed, left, right, closed_left, closed_right, mid, open_left, open_right
i.left
0.1
i.right
0.2
更改pip安装包的源
国内有一些镜像,在安装时使用这些镜像会加快下载的速度,可参考这里。
临时修改(安装时指定):
pip install scrapy -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
永久修改(安装源写入配置文件~/.pip/pip.conf):
[global]
index-url = https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
获取一列数对应的排序
参考Efficient method to calculate the rank vector of a list in Python:
import scipy.stats as ss
ss.rankdata([3, 1, 4, 15, 92])
# array([ 2., 1., 3., 4., 5.])
ss.rankdata([1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5])
# array([ 1., 2., 4., 4., 4., 6., 7.])
计算df中每一列的缺失值比例
参考这里:
percent_missing = df.isnull().sum() * 100 / len(df)
missing_value_df = pd.DataFrame({'column_name': df.columns,
'percent_missing': percent_missing})
在jupyter中使用运行时间
import time
start =time.clock()
#中间写上代码块
end = time.clock()
print('Running time: %s Seconds'%(end-start))
df中分组,将某一列合并为一行
参考这里:
In [326]:
df = pd.DataFrame({'id':['a','a','b','c','c'], 'words':['asd','rtr','s','rrtttt','dsfd']})
df
Out[326]:
id words
0 a asd
1 a rtr
2 b s
3 c rrtttt
4 c dsfd
In [327]:
df.groupby('id')['words'].apply(','.join)
Out[327]:
id
a asd,rtr
b s
c rrtttt,dsfd
Name: words, dtype: object
# 注意,这里是有两行,所以以id进行group之后,只剩下word
# groupby之后是得到一个df
# groupby()[col]是选取对应的column,但是选出的column是series,不是直接的list
df.groupby('photo_id')['like_flag'].apply(lambda x: np.cumsum(list(x))).to_dict()
对于数组计算累计值
参考这里:
import numpy as np
a = [4,6,12]
np.cumsum(a)
#array([4, 10, 22])
对于df指定列,找出最接近某个输入值的行
参考这里:
num
0 1
1 6
2 4
3 5
4 2
input = 3
# 这里是选取的最接近的前2个,控制index可选择1个等
df.iloc[(df['num']-input).abs().argsort()[:2]]
num
2 4
4 2
使用模块管理工具importlib
构建文件目录:
gongjing@bjzyx-c451:~/gj_py_func $ pwd
/home/gongjing/gj_py_func
gongjing@bjzyx-c451:~/gj_py_func $ lst
.
|-list.py
|-file.py
|-dataframe.py
|-init.py
|-__pycache__
| |-list.cpython-37.pyc
| |-file.cpython-37.pyc
| |-dataframe.cpython-37.pyc
| |-load_packages.cpython-37.pyc
|-.ipynb_checkpoints
| |-file-checkpoint.py
| |-dataframe-checkpoint.py
| |-list-checkpoint.py
调用:
import importlib, sys
if '/home/gongjing/' not in sys.path: sys.path.append('/home/gongjing/')
func_df = importlib.import_module('.dataframe', package='gj_py_func')
func_file = importlib.import_module('.file', package='gj_py_func')
func_ls = importlib.import_module('.list', package='gj_py_func')
importlib.reload(func_df)
importlib.reload(func_file)
importlib.reload(func_ls)
# 查看模块信息,包含哪些函数
help(func_df)
Help on module gj_py_func.dataframe in gj_py_func:
NAME
gj_py_func.dataframe
FUNCTIONS
df_col_missing_pct(df)
df_col_sum(df)
df_norm_by_colsum(df)
df_norm_by_rowsum(df)
df_row_sum(df)
load_data(fn, col_ls=None)
FILE
/home/gongjing/gj_py_func/dataframe.py
对df中缺失值进行填充
参考这里:
df.fillna({1:0}, inplace=True)
df[1].fillna(0, inplace=True)
csv写文件时全为逗号隔开的
参考这里:
if item:
JD = item.group()
csvwriter.writerow(JD)
# J,D,",", ,C,o,l,u,m,b,i,a, ,L,a,w, ,S,c,h,o,o,l,....
# one string per row
csvwriter.writerow([JD])
设置.pythonrc文件在打开python console时自动执行
参考这里:
1, 写.pythonrc文件
print("how_use_pythonstartup")
2, 设置PYTHONSTARTUP变量
export PYTHONSTARTUP=~/.pythonrc
3, 打开新的console
Python 2.7.6 (default, Nov 23 2017, 15:49:48)
[GCC 4.8.4] on linux2
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
how_use_pythonstartup
>>>
If you link this blog, please refer to this page, thanks!
Post link:https://tsinghua-gongjing.github.io/posts/python-tricks.html
Latest articles
Links
- ZhangLab , RISE database , THU life , THU info
- Data analysis: pandas , numpy , scipy
- ML/DL: sklearn , sklearn(中文) , pytorch
- Visualization: seaborn , matplotlib , gallery
- Github: me