目录
聚类任务
- 无监督学习任务
- 聚类(clustering)
- 密度估计(density estimation)
- 异常检测(anomaly detection)
- 聚类
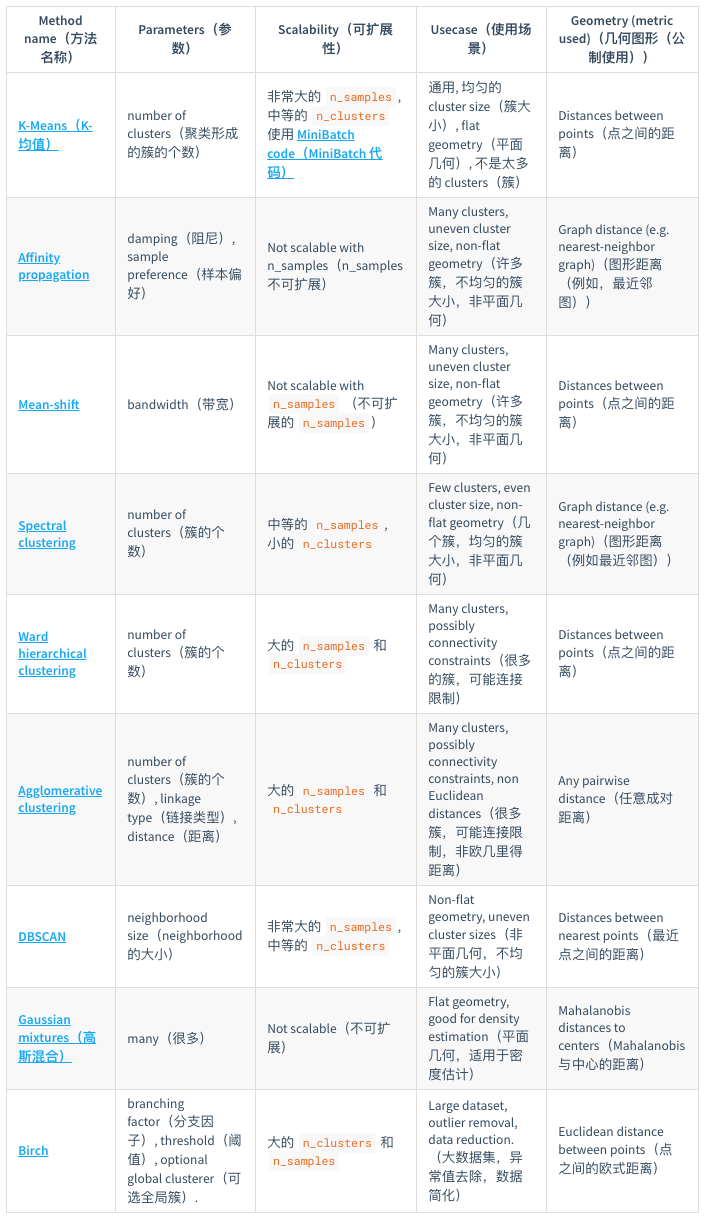
聚类结果的性能度量
- 性能度量:有效性指标(validity index),类似于监督学习中的性能度量
- 什么样的类好?
- 直观:物以类聚
- 归纳:簇内(intra-cluster)相似度高而簇间(inter-cluster)相似度低
- 度量分类:
- 外部指标:external index,将聚类结果与某个参考模型进行比较
- 内部指标:internal index,直接考察聚类结果而不利用任何参考模型
- F值
- 互信息:mutual information
- 平均廓宽:average silhouette width
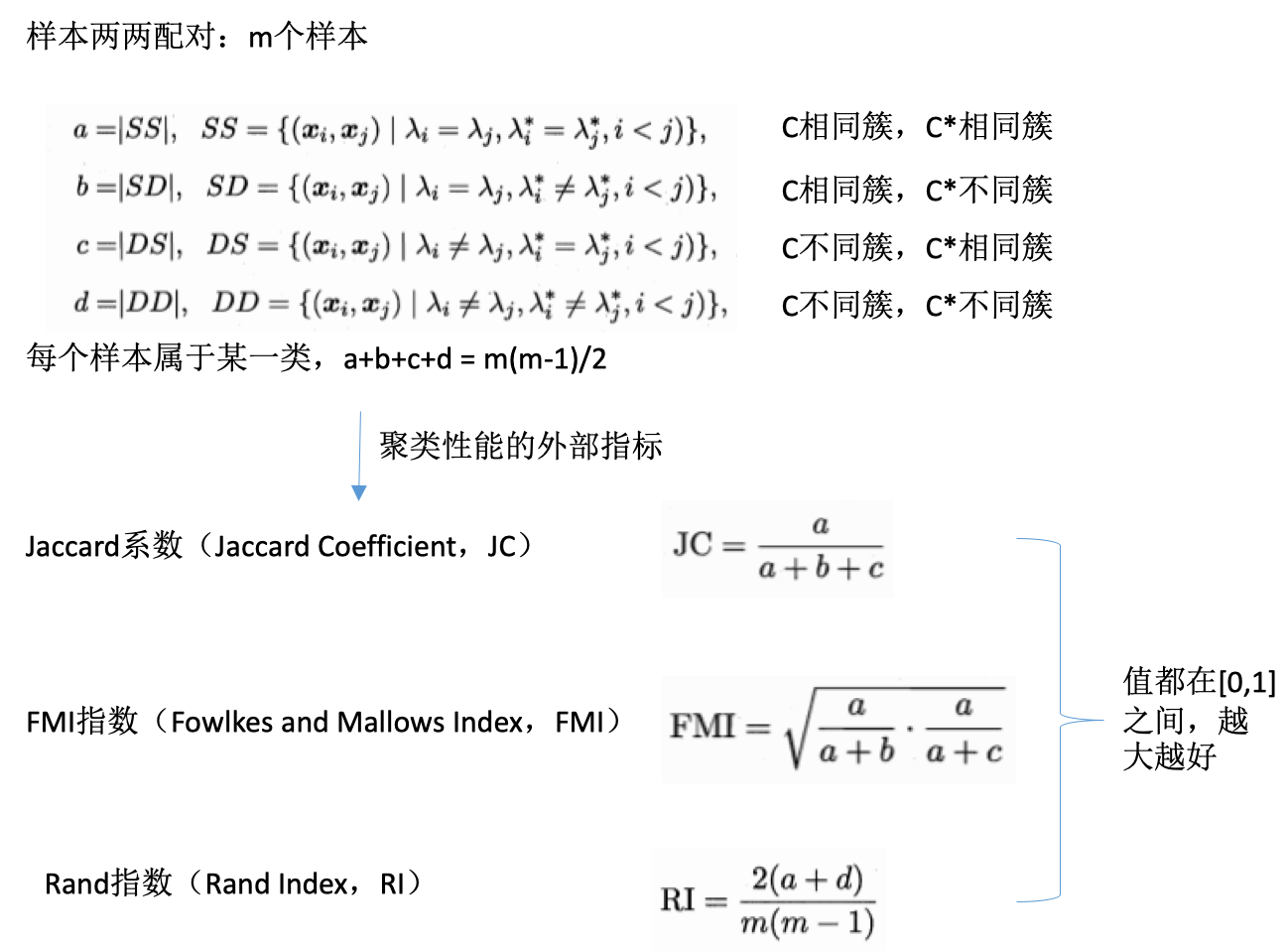
度量:外部指标
定义:
- 数据集:\(D={x_1,x_2,...,x_n}\)
- 聚类结果的簇划分:\(C={C_1,C_2,...,C_n}\)
- 参考模型的簇划分:\(C^*={C^*_1,C^*_2,...,C^*_n}\)
- \(C\)的簇标记向量
- \(C^*\)的簇标记向量
度量:内部指标
距离计算
- 距离度量:样本之间的距离
- 基本性质:
- 非负性:\(dist(x_i,x_j) \geq 0\)
- 同一性:\(dist(x_i,x_j)=0,当且仅当x_i=x_j\)
- 对称性:\(dist(x_i,x_j)=dist(x_j,x_i)\)
- 直递性:\(dist(x_i,x_j) \leq dist(x_i,x_k)dist(x_k,x_j)\)
- 不同的度量:
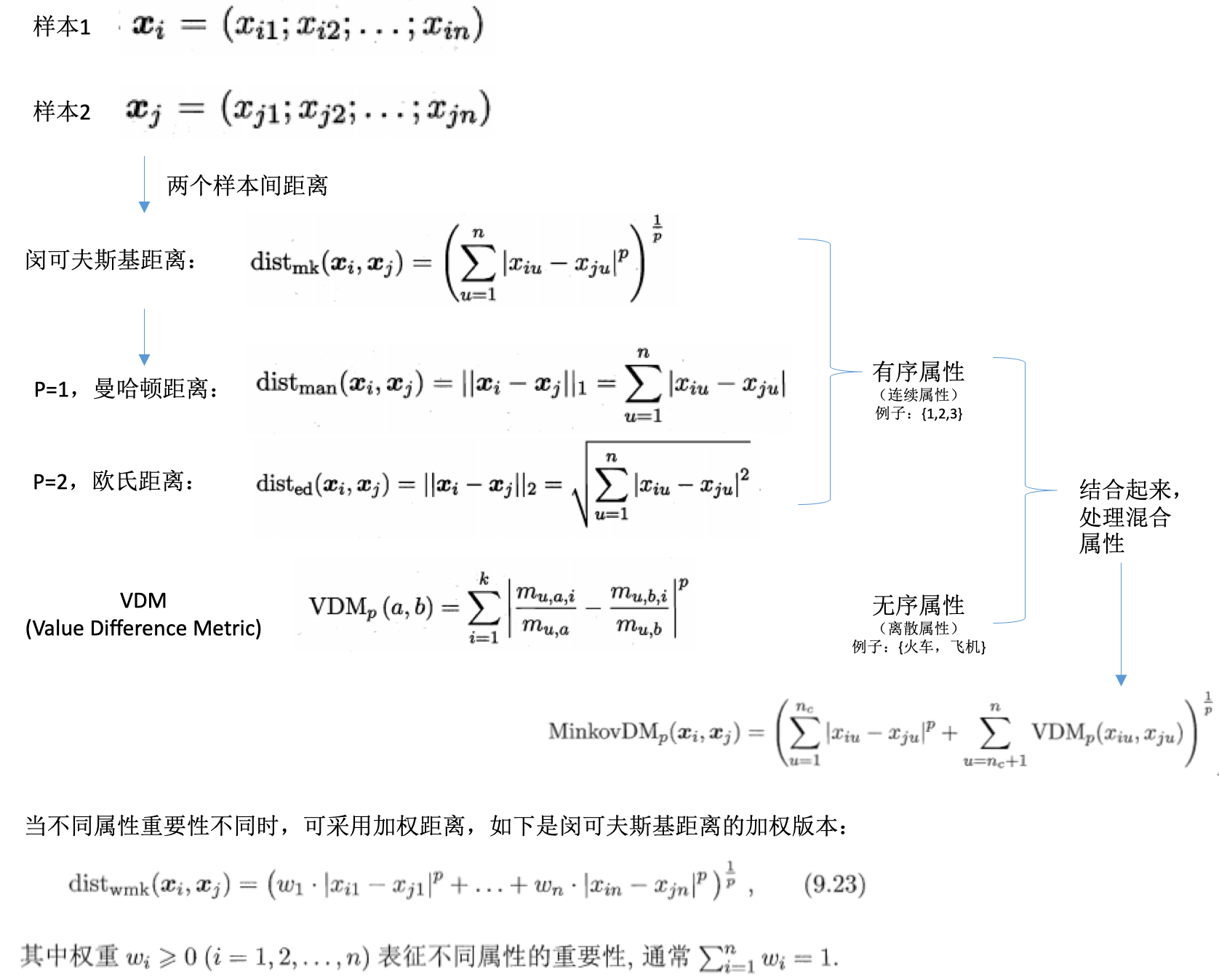
- 还有其他的距离计算方式,比如:
- 內积距离
- 余弦距离
原型聚类
- 原型聚类:基于原型的聚类(prototype-based clustering)
- 原型:样本空间中具有代表性的点
- 基础:假设聚类结构能通过一组原型刻画
k-均值聚类
详细请参见另一篇博文K均值聚类算法,其算法流程如下:
学习向量量化聚类
- 学习向量量化:Learning Vector Quantization, LVQ
- 类似于k均值,寻找一组原型向量
- 但是是假设数据样本带有类别标记,学习的过程中会使用这些标记以辅助聚类
高斯混合聚类
- k均值、LVQ:使用原型向量
- 高斯混合:mixture of gaussian,采用概率模型来表达聚类原型,而非向量
密度聚类
- 密度聚类:density-based clustering
- 基础:假设聚类结构能通过样本分布的紧密程度确定
- 样本密度 -》样本的可连接性,基于可连接样本扩展聚类簇,得到最终聚类结果
- 聚类方法:
- DBSCAN
- OPTICS
- DIANA:自顶向下
DBSCAN
- density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise
- 基于邻域参数刻画样本分布的紧密程度
- 概念:
- 算法流程如下:
层次聚类
- 层次聚类:hierarchical clustering
- 在不同层次对数据集进行划分,从而形成树形的聚类结构
- 聚合策略:自低向上
- 分拆策略:自顶向下
AGNES
- AGNES:AGglomerative NESting
-
自底向上的聚合策略
- 每个样本看成一个簇
- 找出距离最近的两个簇进行合并
-
不断重复,直到达到预设的聚类簇的个数
- 关键:如何计算簇之间的距离。上面介绍的是计算样本之间的距离。
- 簇间距离计算:
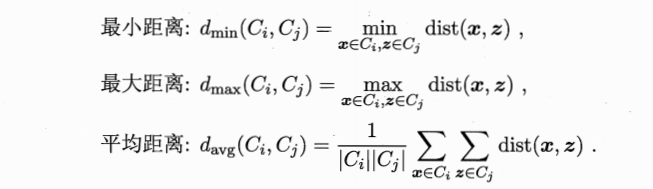
- 可选择不同的距离计算方式
- 最小距离:两个簇的最近样本决定,单链接(single-linkage)
- 最大距离:两个簇的最远样本决定,全链接(complete-linkage)。所以我们通常使用的是全链接,是最大的距离?
- 平均距离:两个簇的所有样本决定,均链接(average-linkage)
- 算法流程:
参考
- 机器学习周志华第9章
If you link this blog, please refer to this page, thanks!
Post link:https://tsinghua-gongjing.github.io/posts/clustering.html
Previous:
Think Stats: probability
Next:
K-近邻算法
Latest articles
Links
- ZhangLab , RISE database , THU life , THU info
- Data analysis: pandas , numpy , scipy
- ML/DL: sklearn , sklearn(中文) , pytorch
- Visualization: seaborn , matplotlib , gallery
- Github: me