How to plot circos graph in RISE database
2018-05-16
Circos plot has been widely used to display genomic element interactions along with annotations. In RISE database we also visualise RNA-RNA interactions in this format.
Here is how we retrieve data from mysql database, process the data into specific format and plot with Circos tool.
login to mysql and check the database information:
[zhangqf5@loginview02 bin]$ ./mysql -h bio04 -uzhangqf5
Warning: Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 1
Server version: 5.6.34-log MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
list available databases:
mysql> show DATABASES;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| RISE |
| test |
+--------------------+
3 rows in set (0.24 sec)
use RISE database and list tables:
mysql> use RISE;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> show tables;
+-----------------------------------------+
| Tables_in_RISE |
+-----------------------------------------+
| auth_group |
| auth_group_permissions |
| auth_permission |
| auth_user |
| auth_user_groups |
| auth_user_user_permissions |
| biomart_hg38 |
| biomart_hg38_mm10_longest |
| biomart_hg38_mm10_longest_chr |
| biomart_mm10 |
| conservation |
| datas_conservation |
| datas_rri |
| django_admin_log |
| django_content_type |
| django_migrations |
| django_session |
| expressionaltasCellLine_mouse |
| gencode_biomart_hg38_mm10_yeast |
| gencode_biomart_hg38_mm10_yeast_repeats |
| gencode_hg38_mm10 |
| human_DARNED |
| human_RADAR |
| human_RMBaseNm |
| human_RMBaseOthers |
| human_RMBasePseudoU |
| human_RMBasem5C |
| human_RMBasem6A |
| human_clipdb |
| human_editing |
| human_modification |
| human_pancan |
| human_ucscSnp142 |
| mouse_clipdb |
| mouse_editing |
| mouse_modification |
| mouse_ucscSnp142 |
| proteinaltasCellLine_human |
| rri |
| rri_bk |
+-----------------------------------------+
40 rows in set (0.00 sec)
columns of specific tables:
mysql> describe rri;
+-----------------------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-----------------------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| index | bigint(20) | YES | MUL | NULL | |
| chr1 | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| start1 | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| end1 | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| chr2 | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| start2 | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| end2 | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| rise_id | varchar(13) | YES | | NULL | |
| score | varchar(15) | YES | | NULL | |
| strand1 | varchar(1) | YES | | NULL | |
| strand2 | varchar(1) | YES | | NULL | |
| ensembl_gene_id1 | varchar(40) | YES | | NULL | |
| ensembl_gene_name1 | varchar(40) | YES | | NULL | |
| ensembl_gene_id2 | varchar(40) | YES | | NULL | |
| ensembl_gene_name2 | varchar(40) | YES | | NULL | |
| ensembl_gene_type1 | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| ensembl_gene_type2 | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| ensembl_gene_abstract_type1 | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| ensembl_gene_abstract_type2 | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| method | varchar(15) | YES | | NULL | |
| species | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| cell_line | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| cell_line2 | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| pubmed_id | text | YES | | NULL | |
| reference | text | YES | | NULL | |
| pos1 | varchar(25) | YES | | NULL | |
| pos2 | varchar(25) | YES | | NULL | |
| chr1_fill | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| start1_fill | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| end1_fill | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| chr2_fill | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| start2_fill | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| end2_fill | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| genomic_context1 | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| genomic_context2 | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| pos1_phastCons | varchar(15) | YES | | NULL | |
| pos1_phyloP | varchar(15) | YES | | NULL | |
| pos2_phastCons | varchar(15) | YES | | NULL | |
| pos2_phyloP | varchar(15) | YES | | NULL | |
+-----------------------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
39 rows in set (0.06 sec)
mysql> describe gencode_biomart_hg38_mm10_yeast_repeats;
+------------------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+------------------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| index | bigint(20) | YES | MUL | NULL | |
| gene_id | text | YES | | NULL | |
| gene_name | text | YES | | NULL | |
| gene_start | bigint(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| gene_end | bigint(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| gene_type | text | YES | | NULL | |
| tx_id | text | YES | | NULL | |
| tx_start | bigint(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| tx_end | bigint(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| tx_type | text | YES | | NULL | |
| tx_abstract_type | text | YES | | NULL | |
| sequence_type | text | YES | | NULL | |
| chr | text | YES | | NULL | |
| start | bigint(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| end | bigint(20) | YES | | NULL | |
+------------------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
15 rows in set (0.01 sec)
run script RISE_circos_plot.py to generate the circos plot:
/Share/home/zhangqf/usr/anaconda/bin/python RISE_circos_plot.py
output files
[zhangqf5@loginview02 duplex_test]$ lt
total 11K
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 394K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.convert.png
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 133K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.convert.resize.html
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 135K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.convert.svg
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 369K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.log
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 258K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.convert.html
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 42K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.anno.convert
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 37K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.genestructure.convert
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 17K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.link.convert
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 5.3K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.linkgenes.convert
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 2.8K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.linkgenes.txt.convert
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 349K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.png
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 135K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.svg
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 232K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.html
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 42K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.anno
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 37K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.genestructure
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 22K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.genestructure.introns
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 19K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.genestructure.introns.txt
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 17K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.link
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 5.3K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.linkgenes
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 2.8K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.linkgenes.txt
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 1.9K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.linkgenes.zooms
-rw-rw---- 1 zhangqf5 zhangqf 2.1K May 16 21:26 ENSG00000100320.linkgenes.zooms2
Note:
ENSG00000100320.convert.png/svg is the final plot correspond to the figure above or in the database for RNA RBFOX2
track files (before log2 transformed): desired file formats are here ENSG00000100320(RBFOX2) as an example
file gene structure:
[zhangqf5@loginview02 duplex_test]$ head -5 ENSG00000100320.genestructure
hs9 94175952 94176043 gene_id=ENSG00000199165,gene_name=MIRLET7A1,gene_type=miRNA,tx_id=ENST00000362295,sequence_type=Exon,id=ENSG00000199165|MIRLET7A1|94175952|94176043|miRNA|ENST00000362295|94175952|94176043|miRNA|miRNA|Exon|9|94175952|94176043
hs10 133246478 133247050 gene_id=ENSG00000166917,gene_name=MIR202HG,gene_type=ncRNA,tx_id=ENST00000553459,sequence_type=Exon,id=ENSG00000166917|MIR202HG|133246478|133247891|antisense|ENST00000553459|133246478|133247891|antisense|ncRNA|Exon|10|133246478|133247050
hs10 133247791 133247891 gene_id=ENSG00000166917,gene_name=MIR202HG,gene_type=ncRNA,tx_id=ENST00000553459,sequence_type=Exon,id=ENSG00000166917|MIR202HG|133246478|133247891|antisense|ENST00000553459|133246478|133247891|antisense|ncRNA|Exon|10|133247791|133247891
hs17 77319515 77320326 gene_id=ENSG00000184640,gene_name=SEPT9,gene_type=protein_coding,tx_id=ENST00000329047,sequence_type=5UTR,id=ENSG00000184640|SEPT9|77280569|77500596|protein_coding|ENST00000329047|77319515|77500592|protein_coding|protein_coding|5UTR|17|77319515|77320326
hs17 77498656 77500592 gene_id=ENSG00000184640,gene_name=SEPT9,gene_type=protein_coding,tx_id=ENST00000329047,sequence_type=3UTR,id=ENSG00000184640|SEPT9|77280569|77500596|protein_coding|ENST00000329047|77319515|77500592|protein_coding|protein_coding|3UTR|17|77498656|77500592
file annotations:
[zhangqf5@loginview02 duplex_test]$ head -5 ENSG00000100320.anno
hs22 35744177 35744178 1 anno_category=modification,anno_source=RMBase,anno_type=m6A,anno_gene_info=chr22|35744164|35744204|RISE0255307_2|2|-|ENSG00000100320|RBFOX2|protein_coding|protein_coding,anno_full=chr22|35744177|35744178|m6A_site_86471|0|-|m6A_site_86471|m6A|1|GSE60213|25799998|RBFOX2&RBFOX2|retained_intron&protein_coding|exon&utr3|GTGAGACCCCTGCAAATGGGACAGCCCCCCAGTTCATGAGG|modification|RMBase|https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25799998|ENSG00000100320|ENST00000405409|3UTR|1,id=chr22|35744164|35744204|RISE0255307_2|2|-|ENSG00000100320|RBFOX2|protein_coding|protein_coding|chr22|35744177|35744178|m6A_site_86471|0|-|m6A_site_86471|m6A|1|GSE60213|25799998|RBFOX2&RBFOX2|retained_intron&protein_coding|exon&utr3|GTGAGACCCCTGCAAATGGGACAGCCCCCCAGTTCATGAGG|modification|RMBase|https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25799998|ENSG00000100320|ENST00000405409|3UTR|1
hs22 35744192 35744193 1 anno_category=modification,anno_source=RMBase,anno_type=m6A,anno_gene_info=chr22|35744164|35744204|RISE0255307_2|2|-|ENSG00000100320|RBFOX2|protein_coding|protein_coding,anno_full=chr22|35744192|35744193|m6A_site_86472|0|-|m6A_site_86472|m6A|1|GSE60213|25799998|RBFOX2&RBFOX2|retained_intron&protein_coding|exon&utr3|CCCTACTGAAGTGACGTGAGACCCCTGCAAATGGGACAGCC|modification|RMBase|https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25799998|ENSG00000100320|ENST00000405409|3UTR|1,id=chr22|35744164|35744204|RISE0255307_2|2|-|ENSG00000100320|RBFOX2|protein_coding|protein_coding|chr22|35744192|35744193|m6A_site_86472|0|-|m6A_site_86472|m6A|1|GSE60213|25799998|RBFOX2&RBFOX2|retained_intron&protein_coding|exon&utr3|CCCTACTGAAGTGACGTGAGACCCCTGCAAATGGGACAGCC|modification|RMBase|https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25799998|ENSG00000100320|ENST00000405409|3UTR|1
hs5 6668743 6668744 1 anno_category=RBP,anno_source=CLIPDB,anno_type=RBP,anno_gene_info=chr5|6668720|6668754|RISE0224410_1|2|+|ENSG00000145545|SRD5A1|protein_coding|protein_coding,anno_full=chr5|6668743|6668744|human_RBP_CLIPdb_iCLIP_CIMS_2234997|0|+|PTBP1|iCLIP&CIMS|HEK293T|GSE57278&GSM1378377|9|25219497|https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25219497|ENSG00000145545|ENST00000510531|3UTR|1|iCLIP|CIMS|human,id=chr5|6668720|6668754|RISE0224410_1|2|+|ENSG00000145545|SRD5A1|protein_coding|protein_coding|chr5|6668743|6668744|human_RBP_CLIPdb_iCLIP_CIMS_2234997|0|+|PTBP1|iCLIP&CIMS|HEK293T|GSE57278&GSM1378377|9|25219497|https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25219497|ENSG00000145545|ENST00000510531|3UTR|1|iCLIP|CIMS|human
hs5 6668704 6668725 1 anno_category=RBP,anno_source=CLIPDB,anno_type=RBP,anno_gene_info=chr5|6668720|6668754|RISE0224410_1|2|+|ENSG00000145545|SRD5A1|protein_coding|protein_coding,anno_full=chr5|6668704|6668725|human_RBP_CLIPdb_iCLIP_CIMS_4297059|0|+|TARDBP|iCLIP&CIMS|Brain|E-MTAB-530&ERR039849|4|21358640|https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21358640|ENSG00000145545|ENST00000510531|3UTR|5|iCLIP|CIMS|human,id=chr5|6668720|6668754|RISE0224410_1|2|+|ENSG00000145545|SRD5A1|protein_coding|protein_coding|chr5|6668704|6668725|human_RBP_CLIPdb_iCLIP_CIMS_4297059|0|+|TARDBP|iCLIP&CIMS|Brain|E-MTAB-530&ERR039849|4|21358640|https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21358640|ENSG00000145545|ENST00000510531|3UTR|5|iCLIP|CIMS|human
hs5 6668749 6668770 1 anno_category=RBP,anno_source=CLIPDB,anno_type=RBP,anno_gene_info=chr5|6668720|6668754|RISE0224410_1|2|+|ENSG00000145545|SRD5A1|protein_coding|protein_coding,anno_full=chr5|6668749|6668770|human_RBP_CLIPdb_iCLIP_CIMS_4435494|0|+|TIAL1|iCLIP&CIMS|HeLa|E-MTAB-432&ERR039780-ERR039783-ERR039784-ERR039785|7|21048981|https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21048981|ENSG00000145545|ENST00000510531|3UTR|5|iCLIP|CIMS|human,id=chr5|6668720|6668754|RISE0224410_1|2|+|ENSG00000145545|SRD5A1|protein_coding|protein_coding|chr5|6668749|6668770|human_RBP_CLIPdb_iCLIP_CIMS_4435494|0|+|TIAL1|iCLIP&CIMS|HeLa|E-MTAB-432&ERR039780-ERR039783-ERR039784-ERR039785|7|21048981|https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21048981|ENSG00000145545|ENST00000510531|3UTR|5|iCLIP|CIMS|human
file links (RRI):
[zhangqf5@loginview02 duplex_test]$ head -5 ENSG00000100320.link
hs5 6668720 6668754 hs22 35740046 35740082 category=GlobalAnalysis,method=PARIS,duplex=derived,gene_id1=ENSG00000145545,gene_name1=SRD5A1,gene_type1=protein_coding,gene_id2=ENSG00000100320,gene_name2=RBFOX2,gene_type2=protein_coding,id=chr5|6668720|6668754|chr22|35740046|35740082|RISE0224410|2|+|-|ENSG00000145545|SRD5A1|ENSG00000100320|RBFOX2|protein_coding|protein_coding|protein_coding|protein_coding|PARIS|human|Hela(highRNase)|Hela|27180905|https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27180905|chr5:6668720-6668754|chr22:35740046-35740082|chr5|6668720|6668754|chr22|35740046|35740082|3UTR|3UTR|0.000441176|-0.350088|0.0715833|0.0108889
hs22 35742350 35742375 hs17 41866974 41867001 category=GlobalAnalysis,method=PARIS,duplex=derived,gene_id1=ENSG00000100320,gene_name1=RBFOX2,gene_type1=protein_coding,gene_id2=ENSG00000131473,gene_name2=ACLY,gene_type2=protein_coding,id=chr22|35742350|35742375|chr17|41866974|41867001|RISE0233924|2|-|-|ENSG00000100320|RBFOX2|ENSG00000131473|ACLY|protein_coding|protein_coding|protein_coding|protein_coding|PARIS|human|Hela(highRNase)|Hela|27180905|https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27180905|chr22:35742350-35742375|chr17:41866974-41867001|chr22|35742350|35742375|chr17|41866974|41867001|3UTR|3UTR|0.2758|0.29404|0.733481|0.895222
hs22 35741848 35741867 hs8 101129130 101129157 category=GlobalAnalysis,method=PARIS,duplex=derived,gene_id1=ENSG00000100320,gene_name1=RBFOX2,gene_type1=protein_coding,gene_id2=ENSG00000253355,gene_name2=KB-1460A1,gene_type2=ncRNA,id=chr22|35741848|35741867|chr8|101129130|101129157|RISE0233925|2|-|+|ENSG00000100320|RBFOX2|ENSG00000253355|KB-1460A1|protein_coding|processed_transcript|protein_coding|ncRNA|PARIS|human|Hela(highRNase)|Hela|27180905|https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27180905|chr22:35741848-35741867|chr8:101129130-101129157|chr22|35741848|35741867|chr8|101129130|101129157|3UTR|Exon|0.000315789|-0.186737|0.0836296|0.0691481
hs22 35741792 35741815 hs6 123471015 123471034 category=GlobalAnalysis,method=PARIS,duplex=derived,gene_id1=ENSG00000100320,gene_name1=RBFOX2,gene_type1=protein_coding,gene_id2=ENSG00000235535,gene_name2=RP11-532N4,gene_type2=ncRNA,id=chr22|35741792|35741815|chr6|123471015|123471034|RISE0233926|2|-|+|ENSG00000100320|RBFOX2|ENSG00000235535|RP11-532N4|protein_coding|antisense|protein_coding|ncRNA|PARIS|human|Hela(highRNase)|Hela|27180905|https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27180905|chr22:35741792-35741815|chr6:123471015-123471034|chr22|35741792|35741815|chr6|123471015|123471034|3UTR|Exon|0.00156522|0.232348|0.0652632|0.296211
hs22 35740318 35740336 hs2 97735297 97735318 category=GlobalAnalysis,method=PARIS,duplex=derived,gene_id1=ENSG00000100320,gene_name1=RBFOX2,gene_type1=protein_coding,gene_id2=ENSG00000115085,gene_name2=ZAP70,gene_type2=protein_coding,id=chr22|35740318|35740336|chr2|97735297|97735318|RISE0233927|2|-|+|ENSG00000100320|RBFOX2|ENSG00000115085|ZAP70|protein_coding|protein_coding|protein_coding|protein_coding|PARIS|human|Hela(highRNase)|Hela|27180905|https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27180905|chr22:35740318-35740336|chr2:97735297-97735318|chr22|35740318|35740336|chr2|97735297|97735318|3UTR|CDS|0.895778|1.97189|0.903|4.62224
file link genes:
[zhangqf5@loginview02 duplex_test]$ head -5 ENSG00000100320.linkgenes
hs9 94175952 94176043 gene_id=ENSG00000199165,gene_name=MIRLET7A1,gene_type=miRNA,tx_id=ENST00000362295,id=ENSG00000199165|MIRLET7A1|94175952|94176043|miRNA|ENST00000362295|94175952|94176043|miRNA|miRNA|Exon|9|94175952|94176043
hs17 41866908 41918987 gene_id=ENSG00000131473,gene_name=ACLY,gene_type=protein_coding,tx_id=ENST00000352035,id=ENSG00000131473|ACLY|41866908|41930542|protein_coding|ENST00000352035|41866908|41918987|protein_coding|protein_coding|5UTR|17|41913874|41913896
hs10 133246478 133247891 gene_id=ENSG00000166917,gene_name=MIR202HG,gene_type=miRNA,tx_id=ENST00000553459,id=ENSG00000166917|MIR202HG|133246478|133247891|antisense|ENST00000553459|133246478|133247891|antisense|ncRNA|Exon|10|133246478|133247050
hs1 629640 630683 gene_id=ENSG00000225630,gene_name=MTND2P28,gene_type=pseudogene,tx_id=ENST00000457540,id=ENSG00000225630|MTND2P28|629640|630683|unprocessed_pseudogene|ENST00000457540|629640|630683|unprocessed_pseudogene|pseudogene|Exon|1|629640|630683
hsX 53556223 53556341 gene_id=ENSG00000271886,gene_name=MIR98,gene_type=miRNA,tx_id=ENST00000606724,id=ENSG00000271886|MIR98|53556223|53556341|miRNA|ENST00000606724|53556223|53556341|miRNA|miRNA|Exon|X|53556223|53556341
generated .conf file, which control the layout of whole plot, e.g., ENSG00000100320.conf
Read full-text »
Motif analysis: MEME suit & HOMER
2018-05-14
- Common tools for motif analysis
- FIMO error: base frequency
- Plot motif logo using meme2img
- TOMOM: identify motif against known motif source
- Prepare .meme file from .fa file
- Multiple peak region (.bed file) overlap
Common tools for motif analysis
-
Motif discovery:
- MEME: Multiple EM for Motif Elicitation, discovers novel, ungapped motifs (recurring, fixed-length patterns) in your sequences (sample output from sequences).
- DREME: Discriminative Regular Expression Motif Elicitation, discovers short, ungapped motifs (recurring, fixed-length patterns) that are relatively enriched in your sequences compared with shuffled sequences or your control sequences (sample output from sequences).
- MEME-ChIP: Motif Analysis of Large Nucleotide Datasets, performs comprehensive motif analysis (including motif discovery) on LARGE (50MB maximum) sets of sequences (typically nucleotide) such as those identified by ChIP-seq or CLIP-seq experiments.
-
Motif scanning:
- FIMO: Find Individual Motif Occurrences, scans a set of sequences for individual matches to each of the motifs you provide.
-
Motif comparison:
- TOMTOM: compares one or more motifs against a database of known motifs (e.g., JASPAR). Tomtom will rank the motifs in the database and produce an alignment for each significant match.
FIMO error: base frequency
根据指定的motif文件,对query的fasta文件,用fimo扫潜在的RBP binding site:
fimo -oc combine_all_full \
--thresh 0.001 \
/Share/home/zhangqf7/gongjing/zebrafish/script/zhangting/paris_RBP/motif_CISBP_RNA_narrow/Collapsed.meme \
combine_all.full.fa
motif .meme 文件的头文件(修改之前):
MEME version 4.10.1
ALPHABET= ACGU
Background letter frequencies (from uniform background):
A 0.25000 C 0.25000 G 0.25000 U 0.25000
报错:
Errors from MEME text parser:
The frequency letter U at position 4 is invalid for the DNA alphabet.
Errors from MEME XML parser:
Expected state IN_MEME not found!
MEME XML parser returned error code 4.
FATAL: No motifs could be read.
motif .meme 文件的头文件(修改之后):
MEME version 4.10.1
ALPHABET= ACGT
Background letter frequencies (from uniform background):
A 0.25000 C 0.25000 G 0.25000 T 0.25000
Plot motif logo using meme2img
[zhangqf7@loginview02 ]$ meme2images
Usage:
meme2images [options] <motifs file> <output directory>
Options:
-motif <ID> output only a selected motif; repeatable
-eps output logos in eps format
-png output logos in png format
-rc output reverse complement logos
-help print this usage message
Description:
Creates motif logos from any MEME or DREME motif format.
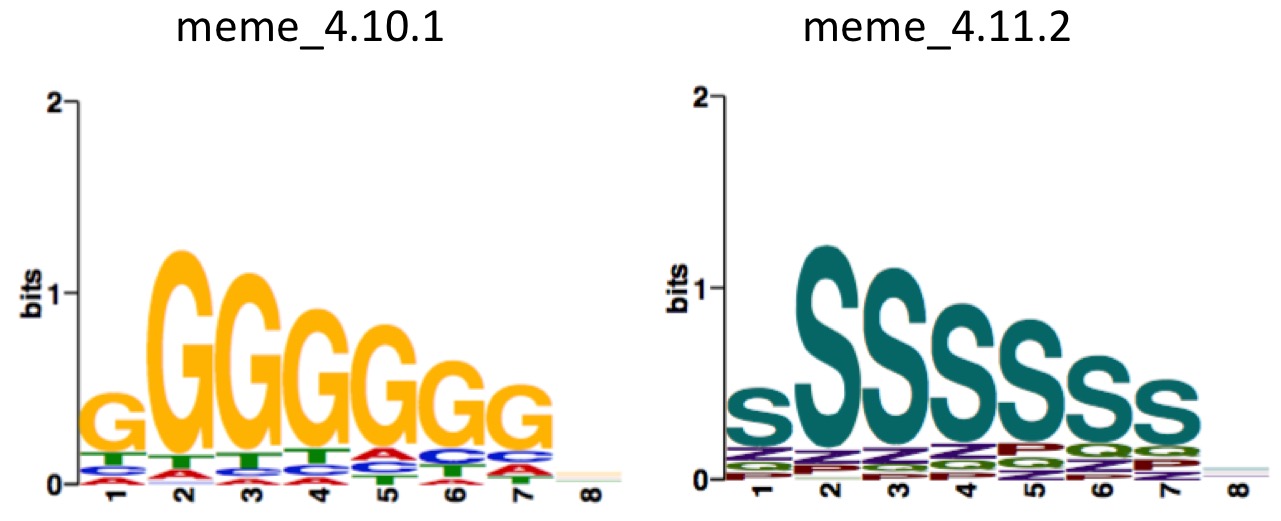
[zhangqf7@loginview02 MolCel2018_RBP]$ cat test.meme
MEME version 4.10.1
ALPHABET
P
Q
S
Z
END ALPHABET
strands: +
MOTIF DGCR8_1_str
letter-probability matrix: alength= 4 w= 8 nsites= 269 E= 3.3e-302
0.096655 0.111524 0.639405 0.152416
0.048326 0.022304 0.866174 0.063196
0.037174 0.044609 0.836433 0.081784
0.052045 0.066914 0.788104 0.092937
0.085501 0.078066 0.765801 0.070632
0.059479 0.130111 0.698886 0.111524
0.122676 0.122677 0.657993 0.096654
0.208179 0.193309 0.397770 0.200743
# generate wrong character
[zhangqf7@loginview02 MolCel2018_RBP]$ which meme2images
/Share/home/zhangqf/usr/meme_4.10.1/bin/meme2images
[zhangqf7@loginview02 MolCel2018_RBP]$ meme2images test.meme -eps test
# generate correct plot
[zhangqf7@loginview02 MolCel2018_RBP]$ /Share/home/zhangqf/usr/meme_4.11.2-app/bin/meme2images test.meme -eps test
TOMOM: identify motif against known motif source
[zhangqf7@loginview02 bin]$ /Share/home/zhangqf7/bin/tomtom --version
5.0.2
# 最新的版本比之前的版本添加了 -norc 参数
# 指定这个参数,只输出正链的,
# 对于扫RNA motif链的方向性很重要(一般不要负链上的)
[zhangqf7@loginview02 bin]$ /Share/home/zhangqf7/bin/tomtom
No query motif database supplied
Usage:
tomtom [options] <query file> <target file>+
Options:
-o <output dir> Name of directory for output files;
will not replace existing directory
-oc <output dir> Name of directory for output files;
will replace existing directory
-xalph Convert the alphabet of the target motif databases
to the alphabet of the query motif database
assuming the core symbols of the target motif
alphabet are a subset; default: reject differences
-bfile <background file>
Name of background file;
default: use the background from the query
motif database
-motif-pseudo <pseudo count>
Apply the pseudocount to the query and target motifs;
default: apply a pseudocount of 0.1
-m <id> Use only query motifs with a specified id;
may be repeated
-mi <index> Use only query motifs with a specifed index;
may be repeated
-thresh <float> Significance threshold; default: 0.5
-evalue Use E-value threshold; default: q-value
-dist allr|ed|kullback|pearson|sandelin|blic1|blic5|llr1|llr5
Distance metric for scoring alignments;
default: pearson
-internal Only allow internal alignments;
default: allow overhangs
-min-overlap <int>
Minimum overlap between query and target;
default: 1
-norc Do not score the reverse complements of targets
-incomplete-scores
Ignore unaligned columns in computing scores
default: use complete set of columns
-text Output in text format (default is HTML)
-png Create PNG logos; default: don't create PNG logos
-eps Create EPS logos; default: don't create EPS logos
-no-ssc Don't apply small-sample correction to logos;
default: use small-sample correction
-verbosity [1|2|3|4]
Set the verbosity of the program; default: 2 (normal)
-version Print the version and exit
$ tomtom -no-ssc
-oc ./tomom_5_Collapsed-used
-verbosity 1
-min-overlap 5
-dist pearson
-evalue
-thresh 5
./dreme.meme
/path/to/motif/source
Prepare .meme file from .fa file
Prepare the .fa file:
[zhangqf7@loginview02 motif_CISBP_RNA_narrow]$ head miR_Family_Info.fa
>let-7
GAGGUAG
>miR-1/206
GGAAUGU
>miR-10
ACCCUGU
>miR-101
ACAGUAC
>miR-103/107
GCAGCAU
The output .meme file (not in order as provides as using dict object):
[zhangqf7@loginview02 motif_CISBP_RNA_narrow]$ head -30 miR_Family_Info.meme
MEME version 4
ALPHABET= ACGT
Background letter frequencies (from uniform background):
A 0.25000 C 0.25000 G 0.25000 T 0.25000
MOTIF miR-214 (miR-214)
letter-probability matrix: alength= 4 w= 7 nsites= 20 E= 0
0 1 0 0
1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 1 0 0
1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 0 1 0
MOTIF miR-217 (miR-217)
letter-probability matrix: alength= 4 w= 7 nsites= 20 E= 0
1 0 0 0
0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1
0 0 1 0
0 1 0 0
1 0 0 0
0 0 0 1
MOTIF miR-740 (miR-740)
The script:
from pyfasta import Fasta
def read_fa(fa):
fa_dict1 = Fasta(fa, key_fn=lambda key: key.split("\t")[0])
fa_dict = {i.split()[0]: j[0:] for i, j in fa_dict1.items()}
print fa_dict.keys()[0:3]
return fa_dict
def write_pwm(seq=None, motif_name=None):
if seq is None:
seq = 'AGGUAAGU'
if motif_name is None:
motif_name = 'Novel'
s = 'MOTIF %s (%s)'%(motif_name, motif_name)
s += '\n\n'
s += 'letter-probability matrix: alength= 4 w= %s nsites= 20 E= 0'%(len(seq))
s += '\n'
for n in seq:
n_s = [1 if n.upper() == b else 0 for b in ['A', 'C', 'G', 'U']]
s += ' '+'\t'.join(map(str, n_s))
s += '\n'
s += '\n'
return s
def meme_header():
header = 'MEME version 4\n\nALPHABET= ACGT\n\nBackground letter frequencies (from uniform background):\nA 0.25000 C 0.25000 G 0.25000 T 0.25000\n\n'
return header
def write_fa_all(fa=None):
savefn = fa.replace('.fa', '.meme')
SAVEFN = open(savefn, 'w')
fa_dict = read_fa(fa)
s_all = ''
header = meme_header()
s_all += header
for i in fa_dict:
seq = fa_dict[i]
s = write_pwm(seq, motif_name=i)
s_all += s
print >>SAVEFN, s_all
SAVEFN.close()
def main():
# header = meme_header()
# s = write_pwm()
# print header + s
write_fa_all()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Multiple peak region (.bed file) overlap
-
biostar: Tutorial: Visualization of ChIP-Seq peak overlaps using HOMER mergePeaks and UpSetR
-
github: Calling mergePeaks to calculate overlap and UpSetR to plot
-
HOMER mergePeaks: Finding Overlapping and Differentially Bound Peaks
# Quick example
# calculate overlapping
mergePeaks H3K27AC.bed \
H3K27ME3.bed \
H3K4ME3.bed \
H3K9AC.bed \
gencode.bed \
-prefix mergepeaks \
-venn venn.txt \
-matrix matrix.txt
# plot overlapping
# SampleID:: output file name (same dir as venn.txt)
Rscript --vanilla multi_peaks_UpSet_plot.R "SampleID" venn.txt
The number of merged peaks are less than original peaks number, as overlapping regions will bed merged (asked in biostar: HOMER mergePeaks totals don’t add up to peaks input):
# original: two entry region overlapped
NM_001017557 1092 1121 NM_001017557 84 1373 + cds *
NM_001017557 1111 1139 NM_001017557 84 1373 + cds *
# merge: the two regions are merged
# in this case, the final number of entry is <= original
Merged-NM_001017557-1116-2 NM_001017557 1093 1139 + 0.000000 window.bed 2 NM_001017557--18,NM_001017557--19
The example venn.txt file output is as below:
H3K27AC.bed H3K27ME3.bed H3K4ME3.bed H3K9AC.bed gencode.bed Total Name
X X 1690 H3K27AC.bed|H3K27ME3.bed
X X X 758 H3K27AC.bed|H3K27ME3.bed|gencode.bed
X X X 147 H3K27AC.bed|H3K27ME3.bed|H3K9AC.bed
X X X X 87 H3K27AC.bed|H3K27ME3.bed|H3K9AC.bed|gencode.bed
X X X 1420 H3K27AC.bed|H3K27ME3.bed|H3K4ME3.bed
X X X X 1797 H3K27AC.bed|H3K27ME3.bed|H3K4ME3.bed|gencode.bed
X X X X 1187 H3K27AC.bed|H3K27ME3.bed|H3K4ME3.bed|H3K9AC.bed
We can also calculate the cross-way percentage using these scripts, which is comparable with the section Display cross-way percentage for each set
import pandas as pd
from nested_dict import nested_dict
import matplotlib as mpl
mpl.use('Agg')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.colors as mcolors
sns.set(style="ticks")
sns.set_context("poster")
def load_upset_file(txt=None, header_ls=None,):
if txt is None:
txt = '/Share/home/zhangqf7/gongjing/zebrafish/result/dynamic_merge_region/005_005_new/abs/venn.txt'
set_category_stat_dict = nested_dict(2, int)
df = pd.read_csv(txt, header=0, sep='\t')
for sample in df.columns[0:-2]:
for label,count,name in zip(df[sample], df['Total'], df['Name']):
if label == 'X' and sample in name:
set_category_stat_dict[sample][len(name.split('|'))] += count
set_category_stat_df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(set_category_stat_dict, orient='index')
set_category_stat_df = set_category_stat_df.loc[df.columns[0:-2], :]
print set_category_stat_df
set_category_stat_df_ratio = set_category_stat_df.div(set_category_stat_df.sum(axis=1), axis=0)
print set_category_stat_df_ratio
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)
set_category_stat_df.plot(kind='bar', stacked=True, ax=ax[0])
set_category_stat_df_ratio.plot(kind='bar', stacked=True, ax=ax[1])
plt.tight_layout()
savefn = txt.replace('.txt', '.ratio.pdf')
plt.savefig(savefn)
plt.close()
def main():
load_upset_file()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
What’s the meaning of -d parameter:
HOMER manual: Maximum distance between peak centers to merge, default: 100
Also asked in biostar HOMER mergePeaks -d value definition: no answer till now.
Prepare the test region bed file:
[zhangqf7@bnode02 abs]$ cat test1.bed
ch1 100 150
[zhangqf7@bnode02 abs]$ cat test2.bed
ch1 70 90
Run using -d 10, the two region are not merged:
[zhangqf7@bnode02 abs]$ mergePeaks test1.bed test2.bed -prefix test10 -venn test10.venn.txt -d 10
Max distance to merge: 10 bp
Merging peaks...
Comparing test1.bed (1 total) and test1.bed (1 total)
Comparing test1.bed (1 total) and test2.bed (1 total)
Comparing test2.bed (1 total) and test1.bed (1 total)
Comparing test2.bed (1 total) and test2.bed (1 total)
[zhangqf7@bnode02 abs]$ cat test10_test1.bed
#name (cmd = mergePeaks test1.bed test2.bed -prefix test10 -venn test10.venn.txt -d 10) chr start end strand Stat Parent files Total subpeakstest1.bed test2.bed
Merged-ch1-125-1 ch1 120 130 + 0.000000 test1.bed 1 default-1
[zhangqf7@bnode02 abs]$ cat test10_test2.bed
#name (cmd = mergePeaks test1.bed test2.bed -prefix test10 -venn test10.venn.txt -d 10) chr start end strand Stat Parent files Total subpeakstest1.bed test2.bed
Merged-ch1-80-1 ch1 75 85 + 0.000000 test2.bed 1 default-1
[zhangqf7@bnode02 abs]$ cat test10.venn.txt
test1.bed test2.bed Total Name
X 1 test2.bed
X 1 test1.bed
Run using -d 35, the two region are still not merged:
[zhangqf7@bnode02 abs]$ mergePeaks test1.bed test2.bed -prefix test35 -venn test35.venn.txt -d 35
Max distance to merge: 35 bp
Merging peaks...
Comparing test1.bed (1 total) and test1.bed (1 total)
Comparing test1.bed (1 total) and test2.bed (1 total)
Comparing test2.bed (1 total) and test1.bed (1 total)
Comparing test2.bed (1 total) and test2.bed (1 total)
[zhangqf7@bnode02 abs]$ cat test35.venn.txt
test1.bed test2.bed Total Name
X 1 test2.bed
X 1 test1.bed
For -d less equal than 45, the regions are not merged.
[zhangqf7@bnode02 abs]$ ll test45*
-rw-rw----+ 1 zhangqf7 zhangqf 225 Sep 28 20:00 test45_test1.bed
-rw-rw----+ 1 zhangqf7 zhangqf 223 Sep 28 20:00 test45_test2.bed
-rw-rw----+ 1 zhangqf7 zhangqf 61 Sep 28 20:00 test45.venn.txt
[zhangqf7@bnode02 abs]$ cat test45_test1.bed
#name (cmd = mergePeaks test1.bed test2.bed -prefix test45 -venn test45.venn.txt -d 45) chr start end strand Stat Parent files Total subpeaks test1.bed test2.bed
Merged-ch1-125-1 ch1 103 147 + 0.000000 test1.bed 1 default-1
[zhangqf7@bnode02 abs]$ cat test45_test2.bed
#name (cmd = mergePeaks test1.bed test2.bed -prefix test45 -venn test45.venn.txt -d 45) chr start end strand Stat Parent files Total subpeaks test1.bed test2.bed
Merged-ch1-80-1 ch1 58 102 + 0.000000 test2.bed 1 default-1
If we set -d >=46 here, here is the merged result:
[zhangqf7@bnode02 abs]$ mergePeaks test1.bed test2.bed -prefix test46 -venn test46.venn.txt -d 46
Max distance to merge: 46 bp
Merging peaks...
Comparing test1.bed (1 total) and test1.bed (1 total)
Comparing test1.bed (1 total) and test2.bed (1 total)
Comparing test2.bed (1 total) and test1.bed (1 total)
Comparing test2.bed (1 total) and test2.bed (1 total)
[zhangqf7@bnode02 abs]$ ll test46*
-rw-rw----+ 1 zhangqf7 zhangqf 243 Sep 28 20:01 test46_test1.bed_test2.bed
-rw-rw----+ 1 zhangqf7 zhangqf 57 Sep 28 20:01 test46.venn.txt
[zhangqf7@bnode02 abs]$ cat test46_test1.bed_test2.bed
#name (cmd = mergePeaks test1.bed test2.bed -prefix test46 -venn test46.venn.txt -d 46) chr start end strand Stat Parent files Total subpeaks test1.bed test2.bed
Merged-ch1-102-2 ch1 57 148 + 0.000000 test1.bed|test2.bed 2 default-1 default-1
[zhangqf7@bnode02 abs]$ cat test46.venn.txt
test1.bed test2.bed Total Name
X X 1 test1.bed|test2.bed
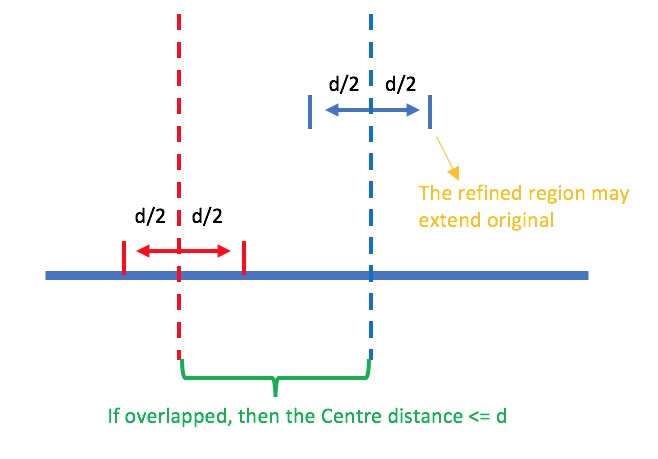
看起来是这样的,当设置一个-d时,会对每一个peak用一个长度等于d的region去替代,然后看替代后的region之间是否有overlap(不是这个的centre),如果有overlap,就merge在一起。因为在-d=45时,替代后的region,首尾相差很小,但是没有overlap,所以没有merge,而取更大的时候,就merge在一起了。如其manual所写,peak centre的距离小于d时会被合并,合并后的起始很大程度会发生改变。
Read full-text »
高通量测序与高性能计算-1-测序技术发展
2018-05-13
- 人类基因组计划(HGP)启动于1990年,6个国家(美国,英国,日本,法国,德国和中国【唯一发展中国家】)的16个研究中心参与,整体计划于2003年完成(中国负责的1%是2001年提前两年完成)。与曼哈顿原子弹计划、阿波罗登月计划称为自然科技史上的“三大计划”。
- HGP的完成主要基于Sanger测序方法。
- 发展中的DNA测序技术:
- 自动测序仪
- 毛细管凝胶电泳测序技术
- 杂交测序技术
- 基因芯片测序技术
- PCR直接测序技术
- cDNA微阵列技术
- 一代测序(经典测序方法):
- 化学降解法:Maxam & Gilbert (1977):随机打断DNA得到片段,在片段的5’端磷酸基团进行放射性标记,然后用不同的化学试剂进行修饰以裂解特定碱基(不同修饰断裂不同碱基),这样得到了一系列长度不同但是5‘起始相同且被标记的DNA片段(共同起点,不同终点),从而知道每个片段所停位置的碱基,不同的片段按照5’-3‘的顺序拼接起来就是所测序列。
- 双脱氧核苷酸末端中止法:Sanger (1977):先随机打断,然后分四管平行反应,每一个管中的ddNTP不同,其他反应物相同,这样特定的ddNTP掺入合成的DNA后,反应终止,形成对应的ddNTP信号的片段(末端碱基为该管中的ddNTP),然后电泳就知道了(四个泳道分别是不同的ddNTP)。
- 影响DNA测序的因素:
- 样本浓度:浓度过高时,起始荧光强度大,拖尾现象严重,荧光标记物很快消耗完,读序短、误差大、可信度低;浓度过低时:荧光信号强度和背景在相当水平,完全区分不开,测序信号不靠谱;
- 样品浓度的鉴定:分光光度法(对PCR产物,需电泳确定条带的特异性:清晰、无杂带、不拖尾);DNA定量仪:A(260/280)~[1.8,2。0], <1.8: 蛋白高, >2.0: RNA高;
- 样品纯度:不纯时信号杂乱不能读取,即使读取出来也只是分析软件的放大作用,错误率很高。其他物质浓度过高、盐浓度过高、TE缓冲液等。
- 二代测序:
- 罗氏454(2005, Genome Sequencer 20 system):(1)文库制备;(2)Emulsion PCR:磁珠结合DNA扩增;(3)测序反应:配对释放焦磷酸,生成ATP驱动释放荧光信号;(4)数据分析。
- Illumina Solexa:(1)文库制备;(2)产生DNA簇:固定于芯片上进行桥式扩增;(3)测序:边合成边测序,荧光标记dNTP的,掺入碱基,记录信号,切除“终止子”基团,以进行下一轮掺入;
- ABI SOLiD:利用DNA连接酶在连接过程中读取序列。
- 二代测序的应用:
- 新物种的de novo测序及基因组重测序
- 目标序列捕获技术:较PCR更简单高效;可确定遗传变异
- 环境基因组学研究:主要是微生物
- 表达谱和转录组分析:RNAseq,不用传统的杂交探针;表达量及时间序列的动态变化
- 小RNA研究:读长短、通量高,鉴定新的小RNA
- 表观基因组学研究
- 测序平台的比较:
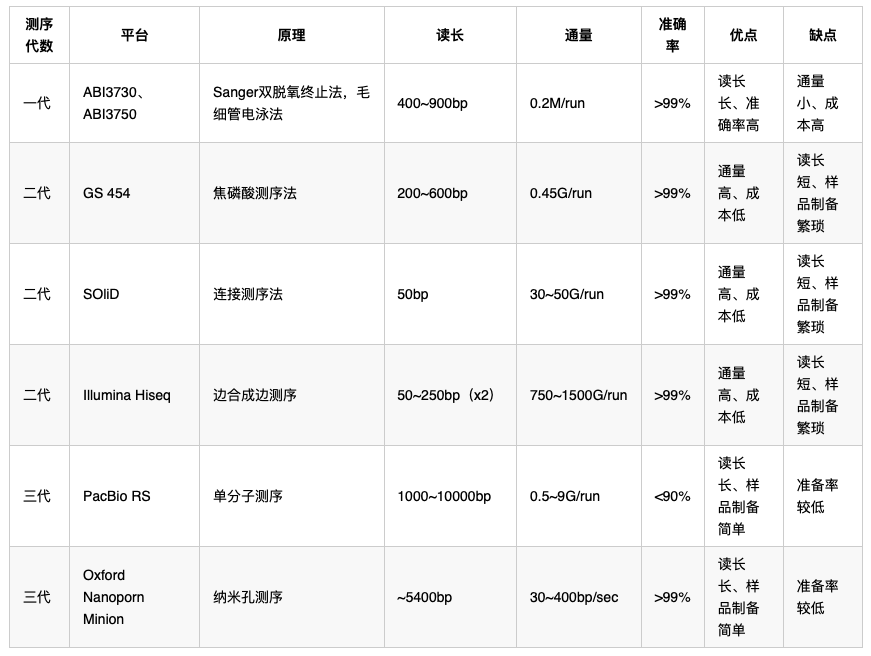
- 三代测序技术:
- Heliscope单分子测序:边合成边测序
- PacBio SMRT(单分子实时测序):芯片含有很多ZMW孔道(DNA聚合酶+片段+荧光标记的dNTP),当合成时,产生对应的磷酸基团的荧光,从而读出信号。
- 纳米孔单分子技术:核酸外切酶切割ssDNA,单个碱基落入纳米孔,与孔内的分子环糊精作用,短暂改变电流强度,从而表征碱基信号。
Read full-text »
高通量测序和高性能计算理论与实践
2018-05-12
最近看到很多公众号文章(图书售卖)在推荐一本介绍测序原理和实践的书籍,主要是北京市计算中心生物学部分的老师们编写的,这是自己读这本书做的一些笔记。
这是本书的目录,基于每一章做一个自己的笔记小结:
1.1 绪论
1.2 测序技术发展历程
1.2.1 发展中的DNA测序技术
1.2.2 经典的DNA测序方法
1.3 Sanger测序技术的原理和流程
1.3.1 Sanger测序技术的原理
1.3.2 Sanger测序技术流程
1.3.3 影响DNA测序的因素
1.4 测序常见问题及分析
1.4.1 PCR产物测序套峰
1.4.2 测序没有信号
1.4.3 测序反应提前终止
1.5 Sanger法测序的应用领域
1.6 第二代测序技术
1.6.1 第二代测序技术的特点
1.6.2 第二代测序技术原理
1.6.3 第二代测序技术的应用
1.6.4 第二代测序技术比较
1.6.5 第二代测序技术存在的问题
1.6.6 第二代测序技术发展及展望
1.7 第三代测序技术
1.7.1 Heliscope单分子测序
1.7.2 单分子实时测序技术
1.7.3 纳米孔单分子技术
1.7.4 第三代单分子测序技术的应用
2.1 De novo测序实验
2.1.1 De novo测序介绍
2.1.2 实验设计
2.1.3 基因组DNA的提取
2.1.4 文库构建
2.2 重测序实验
2.2.1 重测序介绍
2.2.2 重测序常用实验方法
2.2.3 实验设计
2.2.4 文库构建
2.2.5 重测序技术的应用
2.3 转录组测序实验
2.3.1 转录组与转录组学介绍
2.3.2 实验设计
2.3.3 文库构建
2.3.4 验证实验
2.4 宏基因组测序实验
2.4.1 宏基因组学背景介绍
2.4.2 方案设计
2.4.3 常见环境微生物样本制备及DNA提取方法
2.4.4 文库构建
2.4.5 宏基因技术的应用
2.5 MicroRNA测序实验
2.5.1 MicroRNA介绍
2.5.2 实验设计
2.5.3 文库构建
2.5.4 体外实验功能验证
2.5.5 体内实验验证
2.6 LncRNA测序实验
2.6.1 LncRNA介绍
2.6.2 LncRNA实验设计
2.6.3 rRNA去除
2.6.4 文库构建
2.6.5 lncRNA PCR(多基因或单基因验证)
2.6.6 lncRNA的荧光原位杂交(FISH)
2.7 目标区域测序实验
2.7.1 目标区域测序简介
2.7.2 目标区区域测序捕获平台
2.7.3 目标区域测序的实验流程
2.8 表达谱测序实验
2.8.1 表达谱测序技术介绍
2.8.2 实验设计
2.8.3 RNA提取和质量检测
2.8.4 Tag标签制备及测序
2.8.5 DGE差异表达基因的验证
2.8.6 表达谱测序的主要用途
2.8.7 目标基因cDNA全长克隆
2.8.8 荧光定量(RT-PCR)
2.9 甲基化测序实验
2.9.1 DNA甲基化简介
2.9.2 实验设计
2.9.3 甲基化DNA免疫共沉淀测序(MeDIP-Seq)
2.9.4 测序文库构建
2.9.5 甲基化验证实验
3.1 高性能计算环境概述
3.1.1 高性能的发展
3.1.2 高性能集群综合解决方案
3.2 生物信息分析环境搭建
3.2.1 硬件配置
3.2.2 系统安装
3.2.3 系统配置
3.2.4 生物软件安装
3.2.5 生物数据库安装
3.2.6 流程搭建
3.3 生物信息云平台构建及应用
3.3.1 云计算平台概述
3.3.2 生物信息云计算平台发展沿革
3.3.3 生物信息云平台构建
3.3.4 生物信息云平台应用
3.3.5 生物信息云计算平台产品案例
3.3.6 生物信息云计算平台产业发展
3.4 生物信息分析常用资源
3.4.1 NCBI与核酸相关数据库
3.4.2 蛋白质相关数据库
3.4.3 Gene Ontology数据库
3.4.4 KEGG数据库
3.4.5 生物学数据库搭建
3.5 生物信息分析常用的软件
3.5.1 生物数据查看与编辑软件
3.5.2 基于Linux服务器与高性能平台分析软件
3.5.3 高通量测序数据质控软件
3.5.4 序列比对软件
3.5.5 基因组数据拼接软件
3.5.6 变异检测与注释软件
3.5.7 转录组分析软件
3.5.8 R语言
4.1 高通量测序的生物信息学分析概述
4.1.1 高通量测序数据分析的软硬件条件
4.1.2 高通量测序数据分析通用流程
4.2 基因组de novo测序数据分析
4.2.1 De novo测序概述
4.2.2 生物信息分析策略
4.2.3 案例展示
4.2.4 细菌基因组de novo测序拼接流程详解
4.3 基因组重测序数据分析
4.3.1 重测序数据分析概述
4.3.2 重测序数据分析流程
4.3.3 重测序数据分析实践
4.4 转录组测序数据分析
4.4.1 转录组数据分析概述
4.4.2 转录组测序数据基本分析
4.4.3 转录组拼接
4.4.4 鉴定长非编码RNA
4.4.5 鉴定环状RNA
4.4.6 差异表达分析
4.4.7 蛋白结合分析
4.4.8 RNA结构分析
4.4.9 调控网络分析
4.4.10 转录组数据分析典型案例
4.4.11 转录组测序数据分析实践
4.5 宏基因组数据分析
4.5.1 宏基因组数据分析概述
4.5.2 宏基因组数据分析策略
4.5.3 基于16S rDNA/18 S rDNA/ITS靶向测序数据分析流程
4.5.4 基于靶向测序数据分析典型案例
4.5.5 宏基因组测序数据分析流程
4.5.6 宏基因组测序数据分析典型案例
4.6 miRNA测序数据分析
4.6.1 数据分析流程
4.6.2 数据分析典型案例
4.6.3 miRNA测序数据分析实践
4.7 外显子组测序数据分析
4.7.1 外显子测序概述
4.7.2 外显子组测序数据分析流程
4.7.3 外显子组测序数据分析典型案例
4.7.4 外显子组测序在疾病研究中的应用
4.7.5 目标区域测序
4.8 DNA甲基化测序数据分析
4.8.1 DNA甲基化概述
4.8.2 甲基化DNA免疫共沉淀测序
4.8.3 甲基化数据分析示例
4.8.4 全基因组重亚硫酸盐测序(WGBS)
4.8.5 简化重亚硫酸盐测序
4.9 染色质免疫共沉淀测序(ChIP-Seq)数据分析
4.9.1 ChIP-Seq概述
4.9.2 ChIP-Seq数据分析流程
4.9.3 Chip-seq数据分析实践
Read full-text »
Manuals of bioinformatics tools
2018-05-09
list of tools
| Tool | Manual | Description |
|---|---|---|
| fastqc | pdf, online | provide a simple way to do some quality control checks on raw sequence data coming from high throughput sequencing pipelines. |
| cutadapt | pdf, online | Cutadapt finds and removes adapter sequences, primers, poly-A tails and other types of unwanted sequence from your high-throughput sequencing reads. |
| Trimmomatic | pdf, online | Trimmomatic is a fast, multithreaded command line tool that can be used to trim and crop Illumina(FASTQ) data as well as to remove adapters. |
| STAR | pdf, online | To align our large (>80 billon reads) ENCODE Transcriptome RNA-seq dataset, we developed the Spliced Transcripts Alignment to a Reference (STAR) software based on a previously undescribed RNA-seq alignment algorithm that uses sequential maximum mappable seed search in uncompressed suffix arrays followed by seed clustering and stitching procedure. |
| Bowtie2 | pdf, online | Bowtie 2 is an ultrafast and memory-efficient tool for aligning sequencing reads to long reference sequences. It is particularly good at aligning reads of about 50 up to 100s or 1,000s of characters to relatively long (e.g. mammalian) genomes. |
| SAM file format | pdf, online | SAM stands for Sequence Alignment/Map format. It is a TAB-delimited text format consisting of a header section, which is optional, and an alignment section. If present, the header must be prior to the alignments.Header lines start with ‘@’, while alignment lines do not. Each alignment line has 11 mandatory fields for essential alignment information such as mapping position, and variable number of optional fields for flexible or aligner specific information. |
| Bedtools | pdf, online | Collectively, the bedtools utilities are a swiss-army knife of tools for a wide-range of genomics analysis tasks. The most widely-used tools enable genome arithmetic: that is, set theory on the genome. For example, bedtools allows one to intersect, merge, count, complement, and shuffle genomic intervals from multiple files in widely-used genomic file formats such as BAM, BED, GFF/GTF, VCF. While each individual tool is designed to do a relatively simple task (e.g., intersect two interval files), quite sophisticated analyses can be conducted by combining multiple bedtools operations on the UNIX command line. |
Read full-text »
Softwares in daily work
2018-05-04
Here list some of the softwares in work:
| Software | What to do | Local location | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adobe Reader | open pdf, print on noth page mode | AdobeReader-dc-en-a-install.dmg | ***** |
| Alfred | find app, files | Alfred301.dmg, install | ***** |
| Cytoscape | network visualization | Cytoscape-3.4.0-macos.dmg | * |
| Dropbox | sync files | DropboxInstaller.dmg | ***** |
| Endnote X8 | store papers | EndNote-X8-Mac.dmg | ** |
| Evernote | web clip based note | Evernote-RELEASE-6.5-453172.dmg | ** |
| Firefox | test website | Firefox 57.0.1.dmg | *** |
| Foxit Reader | open pdf, can not print on noth page mode | FoxitReader1.11.0301-enu-Setup.pkg | ***** |
| Google Chrome | explore website | googlechrome.dmg | ***** |
| Inkscape | edit picture | Inkscape-0.91-1-x11-10.5-i386_1.dmg | * |
| iTerm 2 | terminal, more powerful | iTerm2-3.0.4.zip | ***** |
| Lantern | free network, not used after SS installed | lantern-installer-beta.dmg | ** |
| MacPyMOL | visulize protein structure | EduPyMOL-v1.7.4.5.dmg | * |
| MagicPrefs | set mouse short keys | ***** | |
| Microsoft Excel | table, simple plot | office2016-mac | ***** |
| Microsoft OneNote | note | office2016-mac | *** |
| Microsoft Word | text file | office2016-mac | ***** |
| Microsoft PowerPoint | ppt, layout picture | office2016-mac | ***** |
| NeteaseMusic | music | NeteaseMusic-1.4.4-470-web.dmg | *** |
| Parallels Desktop | run windows on Mac platform | pd12.2.dmg | ** |
| Prism 6 | generate publishable biology plot | * | |
| communication | QQ_V5.5.1.dmg | ***** | |
| QQ music | music | QQMusicMac_Mgr.dmg | ** |
| RStudio | R coding environment | RStudio-1.1.383.dmg | *** |
| Safari | Mac explorer | ** | |
| Seafile Client | sync file in THU | seafile-client-6.1.7.dmg, manual | ** |
| ShadowsocksX | free network (most stable) | ShadowsocksX-2.6.3.dmg | ***** |
| Skype | meeting | Skype_7.50.461.dmg | ** |
| Sublime Text | code editor | Sublime Text Build 3114.dmg | ***** |
| TeamViewer | screen sharing and control between different computers | TeamViewer.dmg | ** |
| The Unarchiver | de-compress files | ***** | |
| Thunderbird | emails | Thunderbird 45.1.1.dmg | ***** |
| Transmit | file connection between remote server and local | Transmit | ***** |
| VLC | video | vlc-2.2.4.dmg | * |
| communicate, file transfer | ***** | ||
| 搜狗输入法 | for Chinese traditional text | sogou-mac-35e.dmg | ** |
Download:
All the softwares are under dir: /Users/gongjing/SeafileSyn/software/mac.
Also can be accessed online in Tsinghua Cloud
Read full-text »
Soft article in WeChat
2018-05-02
During past few years in THU, I have been involved in several volunteer group. For a member in different team, one ability is to write and edit soft article to introduce the activities. Here list some of the soft articles I wrote and edited with XiuMi:
Read full-text »
Shortcut command in Sublime
2018-05-02
- Text Editing Beginner
- Text Editing Intermediate
- Text Navigation/Goto Anywhere
- General
- Find/Replace
- Split window
- Text manipulation
- Text Selection
- Code Folding and Marks
- Bookmarks
reference: Sublime Text 3 Cheat Sheet
Text Editing Beginner
| Command | Explain |
|---|---|
| ⌃X | Cut line |
| ⌃↵ | Insert line after |
| ⇧⌃↵ | Insert line before |
| ⇧⌃UP | Move line/selection up |
| ⇧⌃DOWN | Move line/selection down |
| ⌃L | Select line - Repeat to select next lines |
| ⌃D | Select word - repeat select other occurrences |
| ⌃M | Go to matching parentheses |
| ⇧⌃M | Select all contents of the current parentheses |
Text Editing Intermediate
| Command | Explain |
|---|---|
| ⌃K⌃K | Delete from cursor to end of line |
| ⌃K⌃BACKSPACE | Delete from cursor to start of line |
| ⌃] | Indent current line(s) |
| ⌃[ | Un-indent current line(s) |
| ⇧⌃D | Duplicate line(s) |
| ⌃J | Join line below to the end of the current line |
| ⌃/ | Comment/un-comment current line |
| ⇧⌃/ | Block comment current selection |
| ⌃Y | Redo or repeat last keyboard shortcut command |
| ⇧⌃V | Paste and indent correctly |
| ⌃[SPACE] | Select next auto-complete suggestion |
| ⌃U | Soft undo |
Text Navigation/Goto Anywhere
| Command | Explain |
|---|---|
| ⌃P | Quick-open files by name |
| ⌃; | Goto word in current file |
| ⌃R | Goto symbol |
| ⌃G | Goto line in current file |
General
| Command | Explain |
|---|---|
| ⌥. | Close tag |
| ⌃K⌃C | Scroll to selection |
| ⇧⌃A | Select tag |
| ⇧⌃J | Select indentation |
| ⇧⌃[SPACE] | Select scope |
| ⌃K⌃B | Toggle side bar |
| ⇧⌃P | Command prompt |
Find/Replace
| Command | Explain |
|---|---|
| ⇧F3 | Find previous |
| F3 | Find next |
| ⌃F | Find |
| ⌃H | Replace |
| ⇧⌃F | Find in files |
Split window
| Command | Explain |
|---|---|
| ⇧⌥2 | Split view into two columns |
| ⇧⌥1 | Revert view to single column |
| ⇧⌥5 | Set view to grid (4 groups) |
| ⌃2 | Jump to group 2 |
| ⇧⌃2 | Move file to group 2 |
Text manipulation
| Command | Explain |
|---|---|
| ⌃K⌃L | Transform to lowercase |
| ⌃K⌃U | Transform to uppercase |
| ⇧⌃K | Delete line |
| ⌃BACKSPACE | Delete word backwords |
| ⌃DEL | Delete word forwards |
Text Selection
| Command | Explain |
|---|---|
| ⌥⌃DOWN | Add new line below with cursor |
| ⌃K⌃D | Skip selection |
| ⇧⌃L | Split selection into lines |
| ⌥F3 | Add cursor at all occurrences of a word |
| ⌥⌃UP | Add new line above with cursor |
| ESC | Return to single selection |
Code Folding and Marks
| Command | Explain |
|---|---|
| ⌃K⌃G | Clear mark |
| ⌃K⌃X | Switch location with mark |
| ⌃K⌃A | Select to mark |
| ⌃K⌃[SPACE] | Set mark |
| ⌃K⌃J | Unfold all |
| ⇧⌃] | Unfold code |
| ⇧⌃[ | Fold code |
Bookmarks
| Command | Explain |
|---|---|
| ⌥F2 | Select all bookmarks |
| ⇧F2 | Previous bookmark |
| F2 | Next bookmark |
| ⌃F2 | Toggle bookmark |
Read full-text »
Latest articles
Links
- ZhangLab , RISE database , THU life , THU info
- Data analysis: pandas , numpy , scipy
- ML/DL: sklearn , sklearn(中文) , pytorch
- Visualization: seaborn , matplotlib , gallery
- Github: me